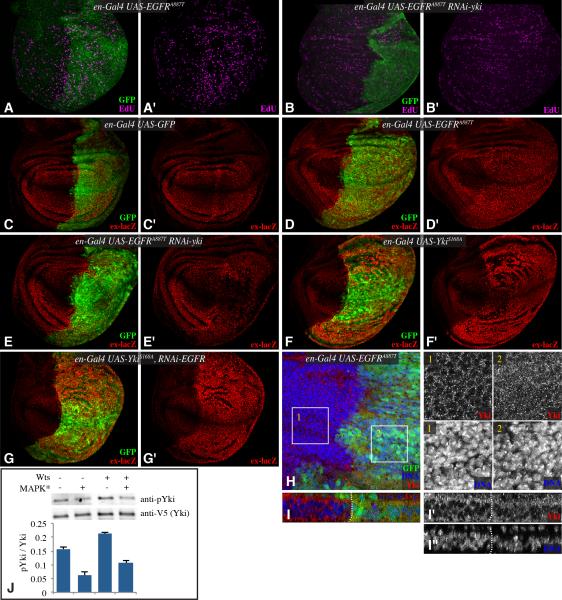
Figure 2. EGFR signaling regulates Yki activity.
(A-G) Third instar wing discs, labeled with EdU (magenta) (A&,B), or β-gal from an ex-lacZ transgene (red) (C-G) and from larvae expressing en-Gal4 UAS-GFP (green) and A) UAS EGFRA887T, B) UAS-EGFRA887T UAS-Yki-RNAi, C) control, D) UAS-EGFRA887T , E) UAS-EGFRA887T UAS-Yki-RNAi, F) UAS-YkiS168A, G) UAS-YkiS168A UAS-EGFR-RNAi. H) Wing disc stained for Yki (red) and DNA (Hoechst, blue) from en-Gal4 UAS-GFP (green) UAS-EGFRA887T. Higher magnifications of single channels of Yki and DNA stains from boxed regions 1 and 2 are shown in black and white at right. I) Vertical section through a portion of the wing disc shown in H. J) Western blots (anti-phospho Ser 168 Yki, anti-V5) on material precipitated using anti-V5 beads from S2 cells transfected to express Yki:V5, and where indicated (MAPK*) pUAS -RasV12, pUAS-Phl, pUAS-Dsor and pUAST-rl constructs, and a Myc:Wts expression plasmid. The histogram at bottom shows quantitation of Yki phosphorylation in transfected cells from multiple experiments, error bars indicate s.d. each of the means is distinct based on one way ANOVA. See also Fig. S1.