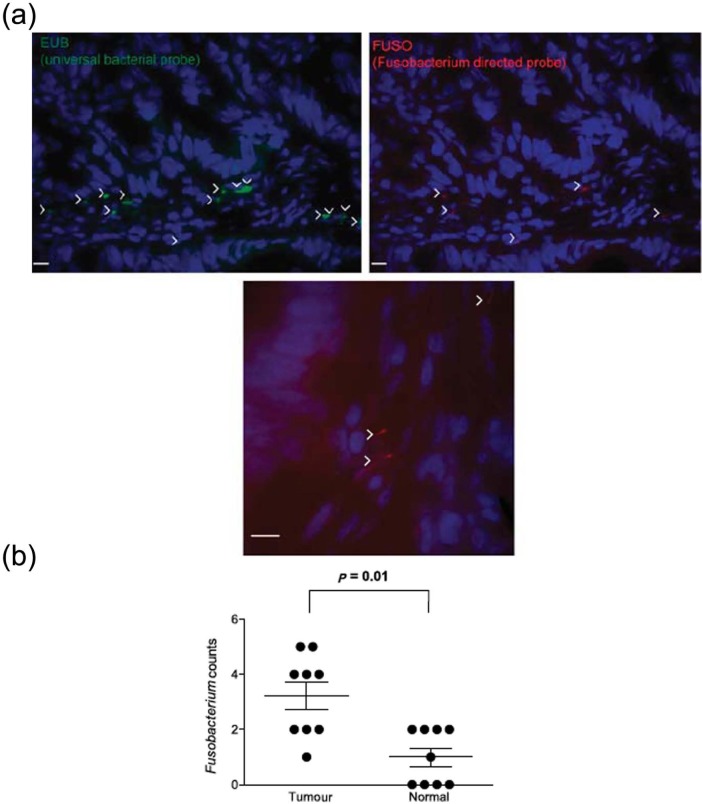
Figure 2.
Fusobacterium in colorectal tumours [Kostic et al. 2012].
(a) Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) using an Oregon-Green 488-conjugated ‘universal bacterial’ 16S rDNA-directed oligonucleotide probe (EUB338, green) (top left), and Cy3-conjugated Fusobacterium (FUSO, red) (top right and bottom centre) 16S rDNA-direct oligonucleotide probe demonstrates the presence of bacteria and Fusobacterium in the colonic mucosa of colorectal tumour samples. Representative images are shown with a 10 μm scale bar in the lower corner of each panel; white arrowheads mark bacteria. Epithelial cell nuclei were stained with 4’,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole. (b) Shows whether Fusobacterium was enriched in tumour versus normal pairs. Each dot represents data from either a tumour or a normal sample from nine tumour/normal paired cases. The mean, standard error of the mean and p values (calculated by a Wilcoxon matched-pair signed rank test) are shown.