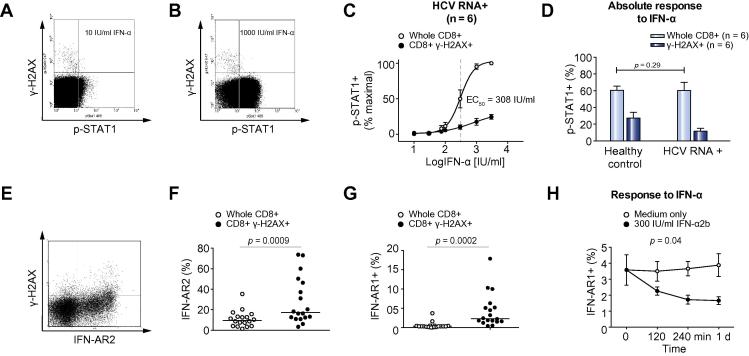
Fig. 3.
CD8+ γ-H2AX+ lymphocytes fail to phosphorylate STAT1 after incubation with IFN-α unrelated to IFN-α receptor function. Circulating T lymphocytes were incubated with variable concentrations of IFN-α2b before staining for CD8, γ-H2AX and pSTAT1 (Tyr 701). Example dot-plots of CD8+ gated T lymphocytes incubated with (A) 10 IU/ml or (B) 1000 IU/ml IFN-α2b. (C) Dose response curves of CD8+ and CD8 + γ-H2AX+ pSTAT1 responses by proportion of pSTAT1 positive cells after incubation with IFN-α in HCV-infected subjects (n = 6). (D) Maximal absolute pSTAT1 response to IFN-α in healthy controls (n = 6) and HCV-infected subjects (n = 6) in different CD8+ lymphocyte subsets defined by γ-H2AX. Analysis by 2-way ANOVA. Failure of CD8 + γ-H2AX + cells to phosphorylate STAT1 does not relate to STAT1 expression or IFN-α receptor components. (E and F) Expression of IFN-AR2 on whole CD8+ and γ-H2AX + CD8+ lymphocytes from HCV-RNA+ subjects (n = 18); (E) example cytometric data of IFN-AR2 and γ-H2AX co-expression; (F) IFN-AR2 expression in whole and γ-H2AX + CD8+ lymphocytes. (G and H). Expression and downregulation of IFN-AR1 on whole CD8+ and γ-H2AX + CD8+ lymphocytes from viraemic HCV infected subjects (n = 18); (G) IFN-AR1 expression in whole and γ-H2AX+ lymphocytes; (H) time course of IFN-AR1 expression in γ-H2AX + CD8+ lymphocytes from HCV-RNA+ subjects (n = 6) cultured in medium alone or with 300 IU/ml IFN-α2b for 24 h. Analysis by 2-way ANOVA.