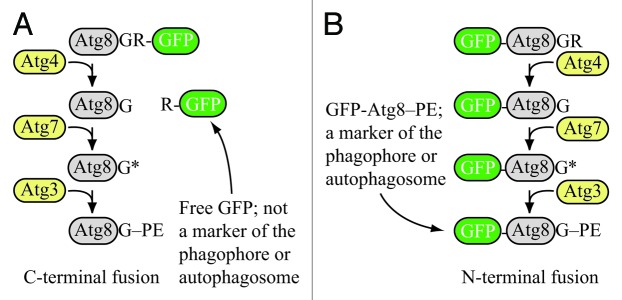
Figure 1. Schematic comparison of the fate of C-terminal versus N-terminal GFP fused to Atg8. (A) If GFP is fused to the C terminus of Atg8 (or LC3), it is removed when Atg4 hydrolyzes the bond between the penultimate glycine residue and arginine. The result is free GFP (with an additional arginine) that does not serve as a marker for the phagophore or autophagosome. However, a C-terminal fusion can be used to monitor Atg4 activity. (B) If GFP is fused to the N terminus of Atg8 (LC3), it remains attached to the protein until vacuolar (lysosomal) delivery; Atg8 is degraded relatively rapidly compared to GFP, so the generation of free GFP in the vacuolar/lysosomal lumen can be used to monitor autophagy activity. Furthermore, the stable GFP-Atg8/LC3 chimera can be used to follow the phagophore or autophagosome. Although the schematic refers to yeast Atg8, essentially the same hold true for LC3 and its related family members.
