Abstract
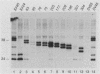
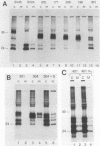
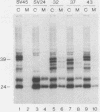
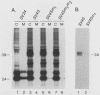
The preS1 surface glycoprotein of hepatitis B virus is targeted to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and is retained in this organelle when expressed in the absence of other viral gene products. The protein is also acylated at its N terminus with myristic acid. Sequences responsible for its ER retention have been identified through examination of mutants bearing lesions in the preS1 coding region. These studies reveal that such sequences map to the N terminus of the molecule, between residues 6 and 19. Molecules in which this region was present remained in the ER; those in which it had been deleted were secreted from the cell. Although all deletions which allowed efficient secretion also impaired acylation of the polypeptide, myristylation alone was not sufficient for ER retention: point mutations which eliminated myristylation did not lead to secretion. These data indicate that an essential element for ER retention resides in a 14-amino-acid sequence that is unrelated to previously described ER retention signals.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G. Intracellular protein topogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1496–1500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattaneo R., Will H., Hernandez N., Schaller H. Signals regulating hepatitis B surface antigen transcription. Nature. 1983 Sep 22;305(5932):336–338. doi: 10.1038/305336a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. C., Smith G. L., Moss B. Hepatitis B virus large surface protein is not secreted but is immunogenic when selectively expressed by recombinant vaccinia virus. J Virol. 1986 Nov;60(2):337–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.2.337-344.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., Buras J., McLachlan A., Popper H., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland C. S., Doms R. W., Bolzau E. M., Webster R. G., Helenius A. Assembly of influenza hemagglutinin trimers and its role in intracellular transport. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1179–1191. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Garber E. A., Pellman D., Hanafusa H. A short sequence in the p60src N terminus is required for p60src myristylation and membrane association and for cell transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1834–1842. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Hepatitis B surface antigen: an unusual secreted protein initially synthesized as a transmembrane polypeptide. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1454–1463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1454. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eble B. E., MacRae D. R., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Multiple topogenic sequences determine the transmembrane orientation of the hepatitis B surface antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3591–3601. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganem D., Varmus H. E. The molecular biology of the hepatitis B viruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:651–693. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gething M. J., McCammon K., Sambrook J. Expression of wild-type and mutant forms of influenza hemagglutinin: the role of folding in intracellular transport. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):939–950. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90076-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horwich A. L., Kalousek F., Mellman I., Rosenberg L. E. A leader peptide is sufficient to direct mitochondrial import of a chimeric protein. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1129–1135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03750.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalderon D., Richardson W. D., Markham A. F., Smith A. E. Sequence requirements for nuclear location of simian virus 40 large-T antigen. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):33–38. doi: 10.1038/311033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. M., Mardon G., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. The first seven amino acids encoded by the v-src oncogene act as a myristylation signal: lysine 7 is a critical determinant. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2435–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. B. Pathways of protein secretion in eukaryotes. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):25–32. doi: 10.1126/science.2994224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld S. Trafficking of lysosomal enzymes in normal and disease states. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):1–6. doi: 10.1172/JCI112262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippincott-Schwartz J., Yuan L. C., Bonifacino J. S., Klausner R. D. Rapid redistribution of Golgi proteins into the ER in cells treated with brefeldin A: evidence for membrane cycling from Golgi to ER. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):801–813. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90685-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Pelham H. R. A C-terminal signal prevents secretion of luminal ER proteins. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):899–907. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Parker K. Identification and chemical synthesis of a host cell receptor binding site on hepatitis B virus. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90663-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palade G. Intracellular aspects of the process of protein synthesis. Science. 1975 Aug 1;189(4200):347–358. doi: 10.1126/science.1096303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Nakamura G. R., Simonsen C. C., Levinson A. D., Brands R. Intracellular assembly and packaging of hepatitis B surface antigen particles occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):884–892. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.884-892.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patzer E. J., Nakamura G. R., Yaffe A. Intracellular transport and secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen in mammalian cells. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):346–353. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.346-353.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellman D., Garber E. A., Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. An N-terminal peptide from p60src can direct myristylation and plasma membrane localization when fused to heterologous proteins. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):374–377. doi: 10.1038/314374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. A frameshift mutation in the pre-S region of the human hepatitis B virus genome allows production of surface antigen particles but eliminates binding to polymerized albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3440–3444. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Inhibition of secretion of hepatitis B surface antigen by a related presurface polypeptide. Science. 1986 Dec 12;234(4782):1388–1391. doi: 10.1126/science.3787251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persing D. H., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. The preS1 protein of hepatitis B virus is acylated at its amino terminus with myristic acid. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1672–1677. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1672-1677.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Rothman J. E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:829–852. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poruchynsky M. S., Atkinson P. H. Primary sequence domains required for the retention of rotavirus VP7 in the endoplasmic reticulum. J Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;107(5):1697–1706. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.5.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Bhat B. M., Wold W. S., Peterson P. A. A short sequence in the COOH-terminus makes an adenovirus membrane glycoprotein a resident of the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90226-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A., McClure M. R., Rice N. R., Luftig R. B., Schultz A. M. Myristylation site in Pr65gag is essential for virus particle formation by Moloney murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7246–7250. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhee S. S., Hunter E. Myristylation is required for intracellular transport but not for assembly of D-type retrovirus capsids. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1045–1053. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1045-1053.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Buss J. E. The covalent modification of eukaryotic proteins with lipid. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sells M. A., Chen M. L., Acs G. Production of hepatitis B virus particles in Hep G2 cells transfected with cloned hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1005–1009. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon K., Lingappa V. R., Ganem D. Secreted hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptides are derived from a transmembrane precursor. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2163–2168. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Ou J. H., Rutter W. J. Assembly of viral particles in Xenopus oocytes: pre-surface-antigens regulate secretion of the hepatitis B viral surface envelope particle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9338–9342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Standring D. N., Rutter W. J., Varmus H. E., Ganem D. Transcription of the hepatitis B surface antigen gene in cultured murine cells initiates within the presurface region. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.563-571.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirzaker S. C., Both G. W. The signal peptide of the rotavirus glycoprotein VP7 is essential for its retention in the ER as an integral membrane protein. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):741–747. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90677-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streuli C. H., Griffin B. E. Myristic acid is coupled to a structural protein of polyoma virus and SV40. Nature. 1987 Apr 9;326(6113):619–622. doi: 10.1038/326619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towler D. A., Gordon J. I., Adams S. P., Glaser L. The biology and enzymology of eukaryotic protein acylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:69–99. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter P., Lingappa V. R. Mechanism of protein translocation across the endoplasmic reticulum membrane. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:499–516. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaginuma K., Shirakata Y., Kobayashi M., Koike K. Hepatitis B virus (HBV) particles are produced in a cell culture system by transient expression of transfected HBV DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]