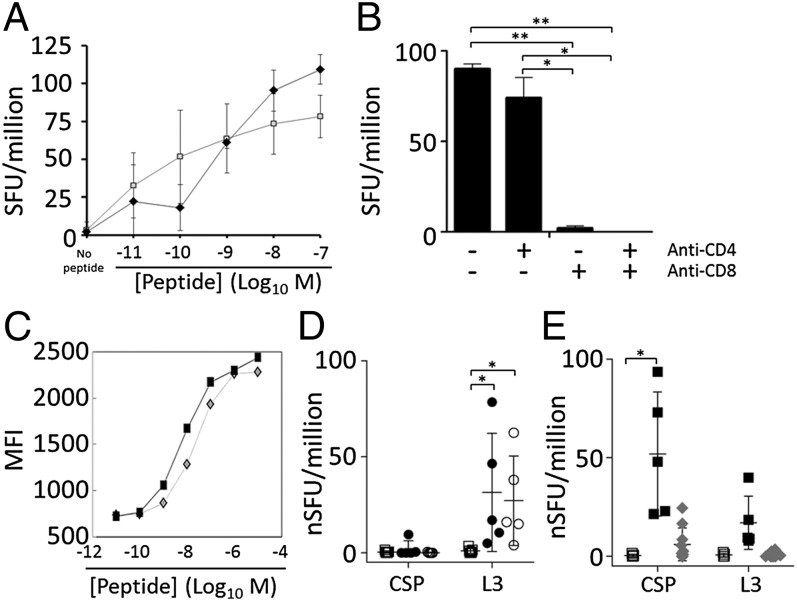
Fig. 3.
The L3-specific response is mediated by CD8+ T cells and can be induced by cross-priming. (A) IFNγ ELISPOT of CPS-immunized BALB/c mice with varied concentrations of CSP (SYVPSAEQI, open squares) or L3 (GYKSGMSHI, filled diamonds) peptides. SFU, IFNγ spot forming units (SFU) per million splenocytes. Compared with no peptide controls, all results were significant at P < 0.05 for all peptide concentrations >1 × 10−9 M (unpaired t test; three samples per data point). (B) Antibodies were used to block CD4 and/or CD8 during the ELISPOT. Error bars show 95% CI; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.001; two samples per group. (C) RMA/S cells expressing H2-Kd were incubated with the designated concentration of CSP (diamonds) or L3 (squares) peptide and monitored to determine the stabilization of H2-Kd. A–C are representative of two experiments each. (D) Mice were immunized with heat-treated uninfected (squares) or infected-erythrocytes (P. yoelii, filled circles; P. berghei, open circles), and 7 d later ELISPOT was performed as in A by using 1 × 10−7 M peptides. Data compiled from two experiments and presented as normalized SFU per million splenocytes (nSFU = SFU minus SFU of mock-treated controls). *P < 0.05 (unpaired t test). (E) Mice immunized with live- (black squares) or heat-treated (gray diamonds) GAP sporozoites were compared with naïve mice (white squares) by ELISPOT as in D. *P < 0.0001 (unpaired t test). In D and E, error bars, SEM; n = 2–3 per experiment for naïve mice and live GAP; n = 5 per experiment for heat-treated iRBCs and heat-treated GAP.