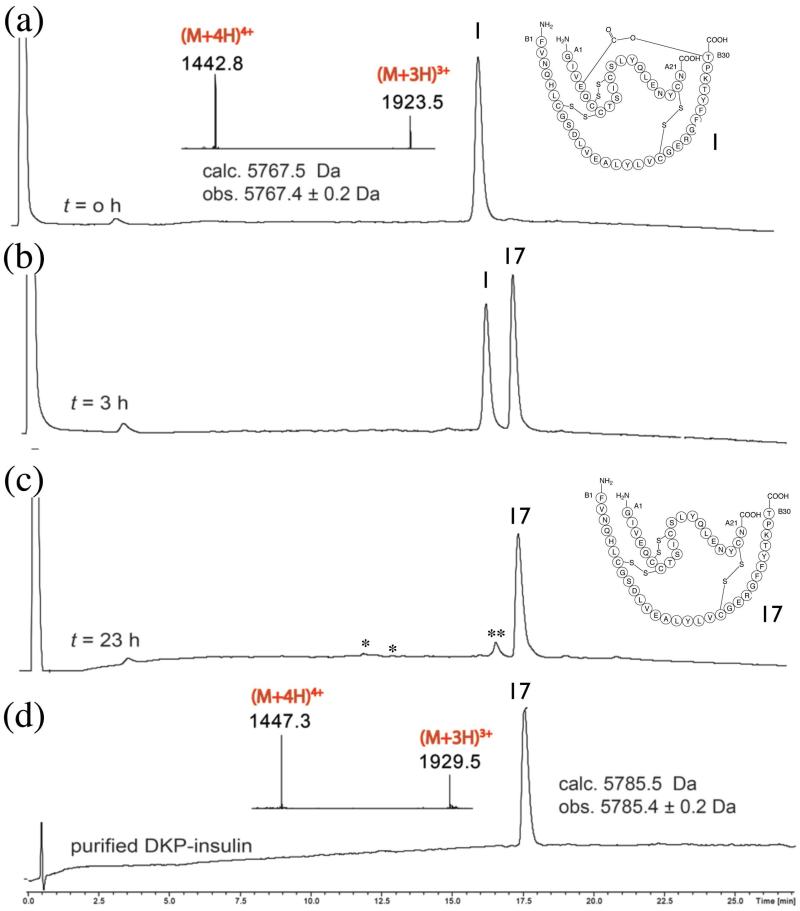
Figure 4. Conversion of DKP ester insulin to native DKP insulin.
Saponification of ester insulin 1 to give DKP insulin 17: (a) Ester insulin 1 at t = o h (Inset: on line ESI-MS spectra of the main peak). (b,c) Reaction mixture at (b) t = 3 h and (c) t = 23 h. *: derived from A chain. **: oxidized B-chain. (d) Purified DKP insulin (Inset: on-line ESI-MS spectra of the main peak). The observed increase of 18 Da for the hydrolyzed DKP insulin confirms the conversion of ester insulin into DKP insulin by addition of the elements of water. The chromatographic separations were performed on a C18 column using a linear gradient (9%–53%) of buffer B in buffer A over 22 min.