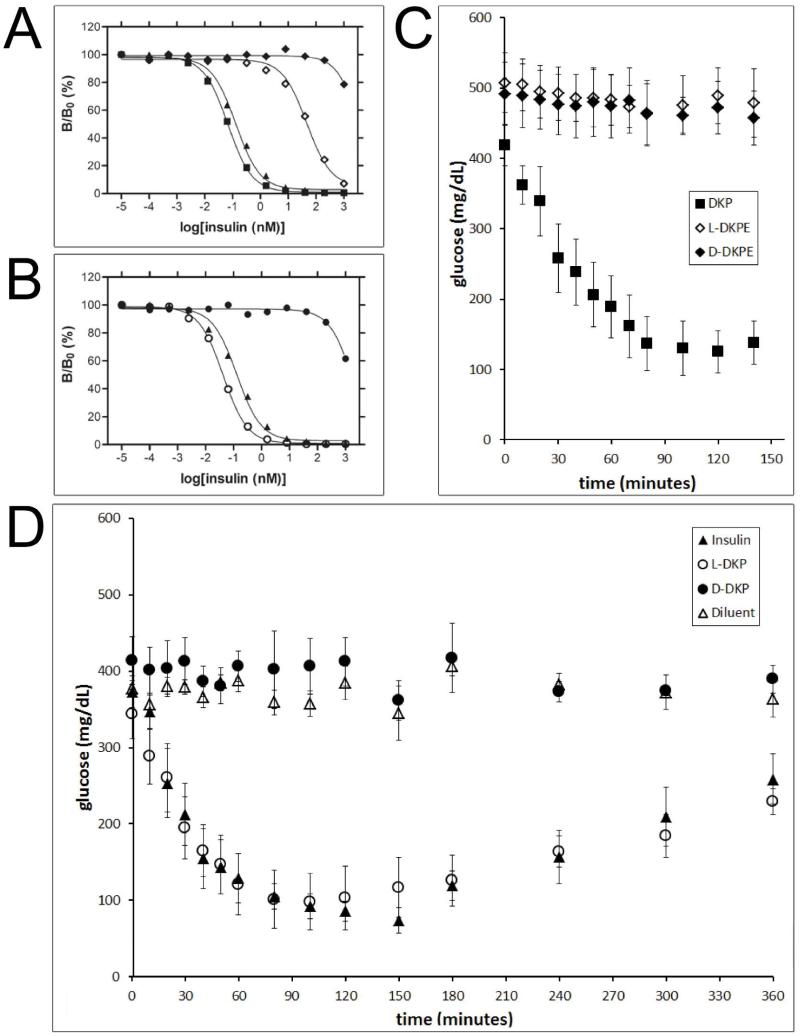
Figure 5. Receptor-binding and diabetic rat assays.
(A) receptor-binding assay: biosynthetic DKP insulin (■), biosynthetic wild-type (wt) insulin (▲), synthetic L-DKP ester insulin (L-DKPE) (◇), synthetic D-DKP ester insulin (D-DKPE) (◆). (B) Receptor-binding assay: biosynthetic wt insulin (▲), synthetic L-DKP insulin (○), synthetic D-DKP insulin (●). (C) Diabetic rat assay: biosynthetic DKP insulin (■), synthetic L-DKPE (◇), synthetic D-DKPE (◆). The experiment presented in panel C was abbreviated since both ester insulins were not active. (D) Diabetic rat assay: biosynthetic wt insulin (▲), synthetic L-DKP insulin (○), synthetic D-DKP insulin (●).“Diluent” (△) in panel D means a buffer control (i.e., no protein). The same symbols have the same meanings throughout.