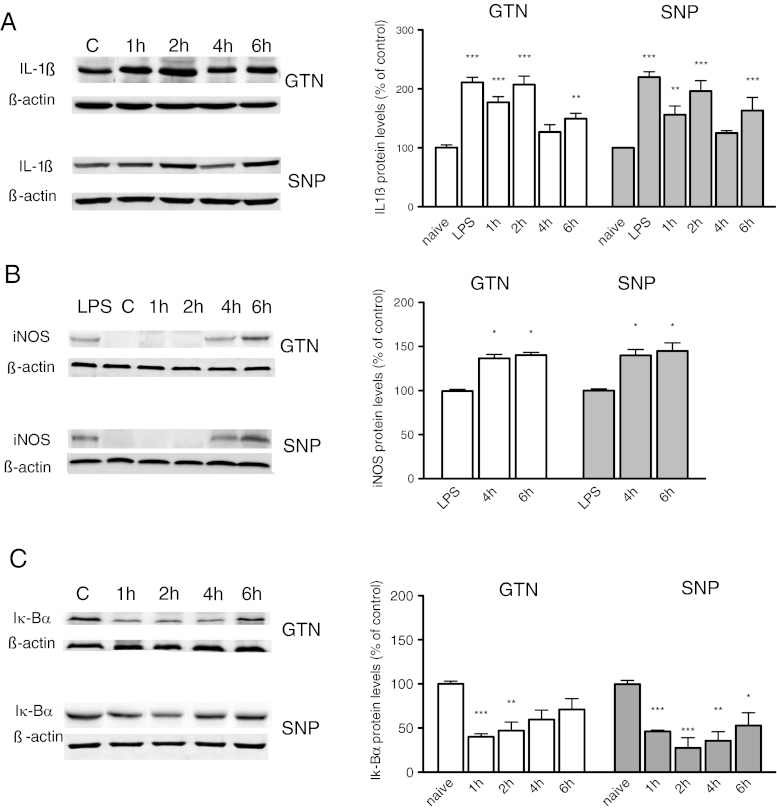
Fig. 2.
Effect of nitric oxide (NO) donors’ administration on interleukin (IL)-1ß, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and Iκ-Bα expression. Protein levels were detected by using an immunoblotting technique. (A) Densitometric measurements of IL-1ß protein expression show a biphasic increase after nitroglycerin (GTN) (10 mg/kg, i.p.; F[4, 18] 19.410) or sodium nitroprusside (SNP) (1 mg/kg i.p.; F[5, 24] 21.740), with a peak protein expression at 1 to 2 h and 6 h. IL-1ß protein expression after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection was used as positive control. (B) iNOS protein was not detected in the control animals (C) or in mice receiving GTN or SNP 1 and 2 h after administration within the dura mater. iNOS protein appeared at 4 and 6 h (GTN F[2, 9] 8.125); SNP (F[2, 9] 8.932). LPS was used as control. (C) NO donors activate meningeal NF-κB pathway, as indicated by the reduced levels of Iκ-Bα (GTN F[4, 15] 17.710; SNP 8F[4, 16] 21.670). The columns represent the densitometric quantitation of immunoreactive protein expressed relative to control. Representative immunoblots were reported in each panel. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 compared with the control group