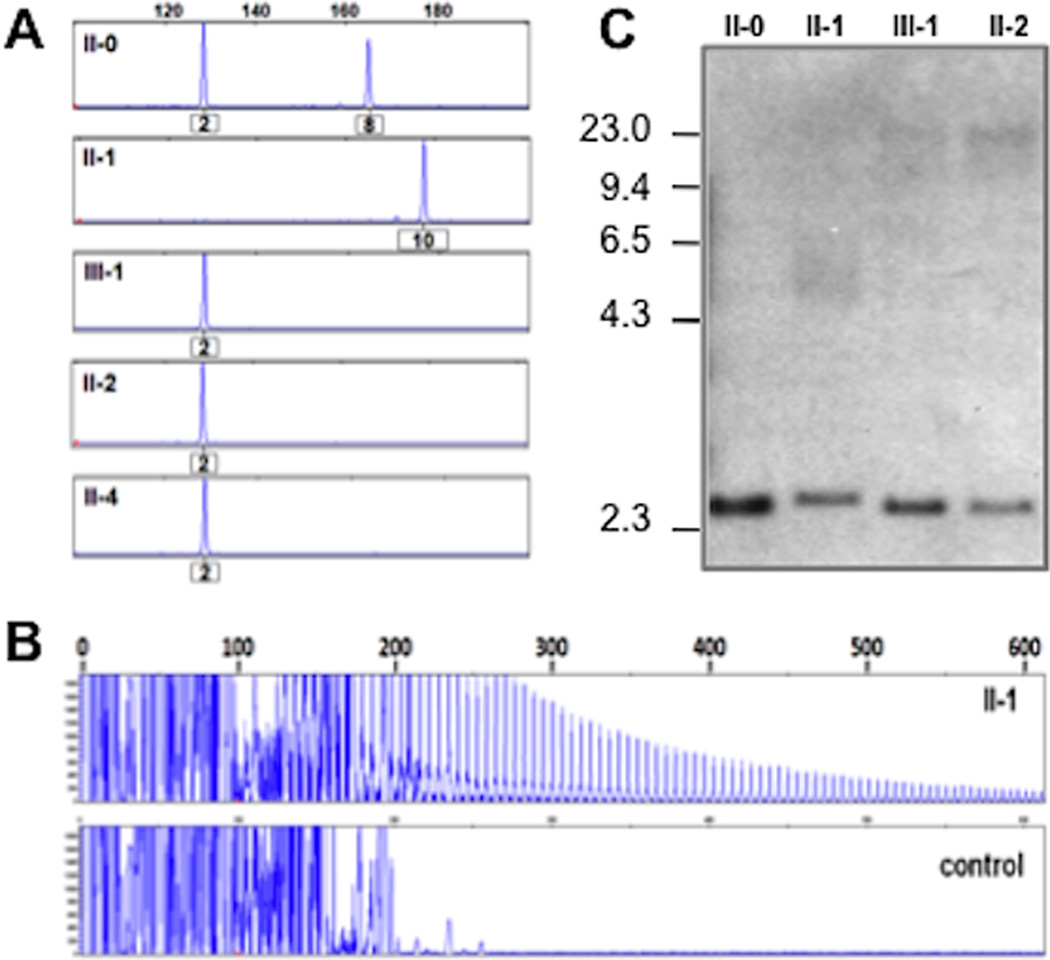
Figure 3. Molecular genetic analyses of C9orf72 repeat expansions in UCSFBR1 family.
Legend: (A) Fluorescent fragment length analysis of a PCR fragment containing the GGGGCC repeat in C9orf72 in 4 patients (II-1, III-1, II-2 and II-4) and one unaffected spouse (II-0). A lack of transmission from the affected parent (II-1) to the affected offspring (III-1) is seen. Numbers under the peaks indicate number of GGGGCC hexanucleotide repeats. (B) PCR products of repeat-primed PCR reactions separated on an ABI3730 DNA Analyzer and visualized by GENEMAPPER software. Electropherograms are zoomed to 2,000 relative fluorescence units to show stutter amplification. One expanded repeat carrier (II-1) and one healthy control are shown. (C) Southern blotting of 3 expanded repeat carriers and one unaffected spouse using genomic DNA extracted from blood. Patients with expanded repeats (II-1, III-1 and II-2) show additional alleles ranging from 5–23 kb, while the normal spouse (II-0) only shows the expected ~2.3 kb wild-type allele.