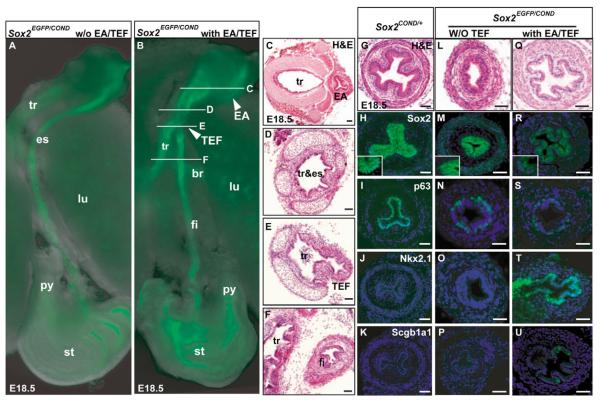
Fig. 2. Tracheoesophageal fistula and esophageal phenotype of Sox2EGFP/COND hypomorphic mutants.
(A,B) Fluorescence microscopy of dissected foregut of Sox2EGFP/COND mutant without (A) and with (B) distal tracheoesophageal fistula (TEF). In B the arrowhead marked EA shows the blind-ended proximal esophagus known in this condition as esophageal atresia (Brunner and van Bokhoven, 2005). White lines indicate level of sections shown in C-F. (C-F) Histological sections through trachea and esophagus of mutant similar to that shown in B. Note the EA in C, and in E the presence of a continuation (TEF) between the dorsal common tube and the distal esophagus (here called the fistula). (G-K) Sections of Sox2COND/+ esophagus demonstrating cellular organization (G), immunohistochemical localization of Sox2, with high-power inset showing strong nuclear staining of basal cells and background cytoplasmic staining of suprabasal cells (H), high p63 in nuclei of basal cells (I) and absence of expression for Nkx2.1 (J) and Scgb1a1 (K). (L-P) Phenotype of esophagus of typical compound mutant without TEF showing cellular organization (note that scale bar is different from G) (L), low Sox2 nuclear staining that is just above background cytoplasmic staining (inset) (M), reduced number of p63-positive cells compared with control (N) and absence of Nkx2.1 and Scgb1a1 (O,P). (Q-U) Phenotype of esophagus of typical compound mutant with TEF, showing cellular organization with a clear monolayered epithelium (Q), absence of Sox2 nuclear staining (R), very few p63-positive cells (S), strong nuclear staining for Nkx2.1 (T) and scattered cells positive for Scgb1a1 (U). Nuclei in H-U are counterstained with DAPI. Scale bars: 100 μm. br, primary bronchus of lung; fi, fistula or distal esophagus; py, pyloric sphincter; tr&es, undivided foregut tube that represents both trachea and esophagus.