Fig. 10.
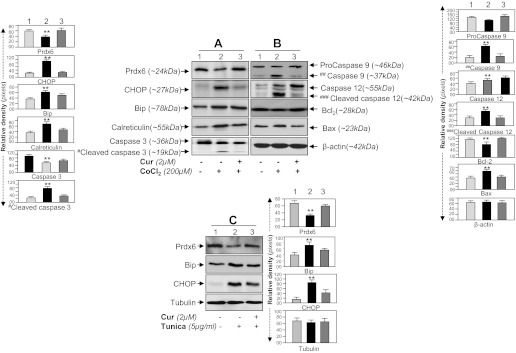
Hypoxia mimic agent, CoCl2, or an ER stressor, tunicamycin, induced aberrant expression of ER stress-responsive proteins in HT22 could be reversed by curcumin. A and B: Western analysis showing reduction of ER stress-responsive proteins in curcumin-treated HT22 cells expressing elevated Prdx6 expression after CoCl2 treatment. Cells were pretreated with curcumin for 12 h followed by CoCl2 (200 μM) exposure. After 48 h, cell lysate was prepared and immunoblotted using different antibodies as shown. An increased expression pattern of Bip, CHOP, calreticulin, and activated forms of caspase 3, caspase 9, and caspase 12 was observed in CoCl2 exposed cells while in presence of curcumin expression of ER stress-responsive protein reduced (A, compare lane 1 vs. 3 and B, lane 1 vs. 3). A, top: Prdx6 expression following curcumin treatment (lane 3). Protein bands were quantified using a densitometer and levels were normalized to corresponding β-actin levels; histograms are shown at left and right of the protein bands. **P < 0.001, statistically significant difference. C: HT22 cells were pretreated with curcumin for 12 h followed by tunicamycin treatment for 48 h. Total cell lysate was prepared and resolved onto 10% SDS gel, and the expression of the ER markers Bip and CHOP was measured. Experiments were done 3 times, and values are represented as means ± SD. **P < 0.001, statistically significant difference.
