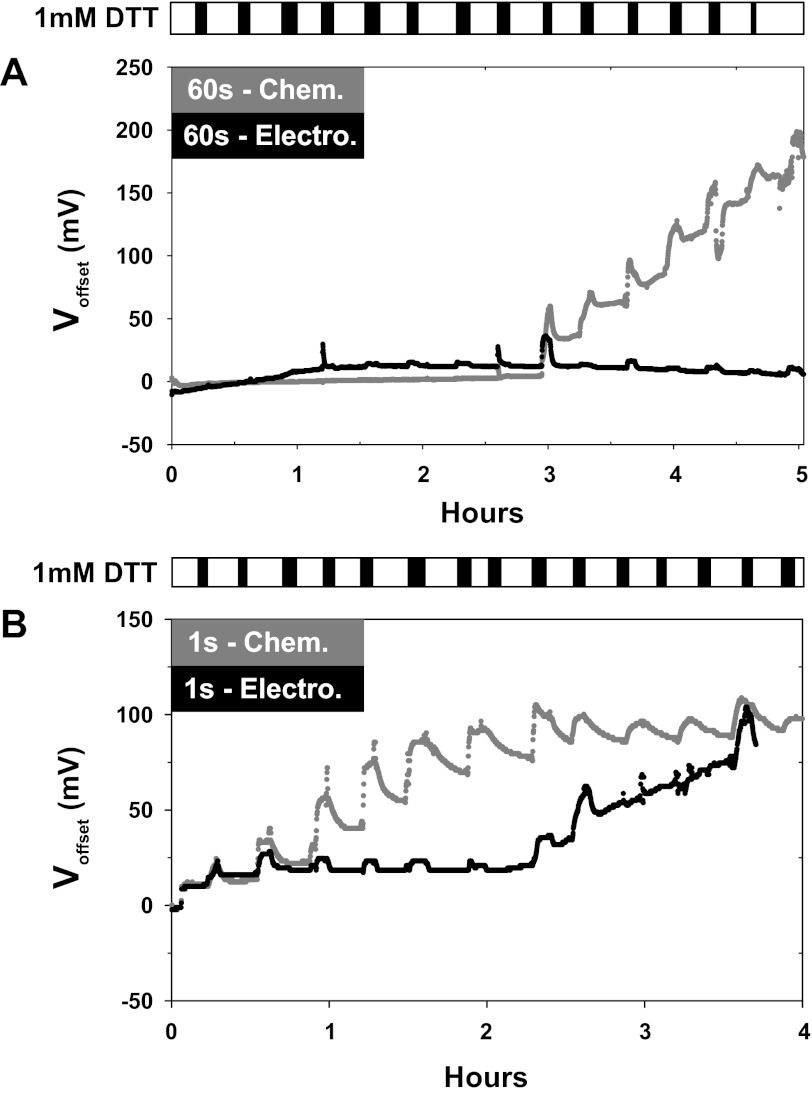
Fig. 3.
Time and use dependent increase in the offsets caused by DTT. Both electrically and chemically chlorided Ag/AgCl electrodes were examined. To simulate use and deplete the layer of deposited AgCl, a −80-μA current was applied to each electrode for the 4–5 h experimental duration. At ∼15-min intervals, DTT was applied for 3–5 min as shown by the scale bar at the bottom. A: electrodes chlorided for 60 s showed no initial effects of DTT for up to 3 h. After this time period, the chemically chlorided Ag/AgCl electrodes developed a >200-mV offset with no effects on the electrically chlorided electrode. B: electrodes chlorided for 1 s showed large offsets in response to DTT with the chemically chlorided electrode developing an offset first. In both cases the electrodes developed offsets were similar in magnitude to those observed with bare silver wires; n = 4 in each group.