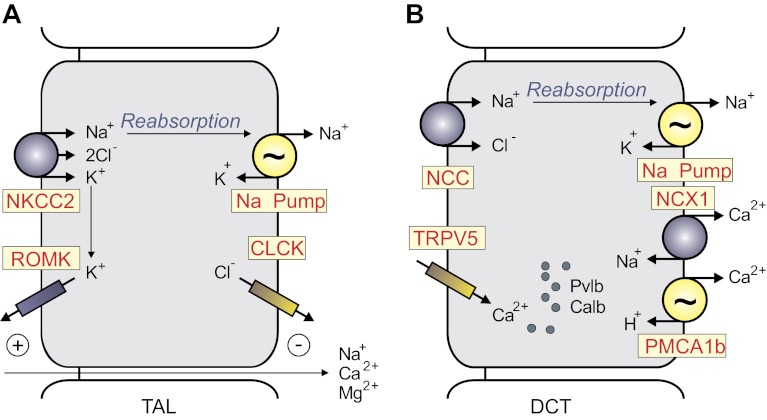
Fig. 4.
Major SLC12 transporters in mammalian kidneys. A: thick ascending limb epithelial cell of the Loop of Henle. NKCC2 participates in the reabsorption of Na+ and recycles the K+ that exits through the ATP-dependent renal outer medullary potassium channel (ROMK). Additional Na+ ions follow the paracellular pathway driven by an electric gradient generated by ROMK on the apical membrane and CLCK (CLCKA and CLCKB) on the basolateral membrane. B: epithelial cell of the distal convoluted tubule (DCT). NCC expressed on the apical membrane contributes to Na+ reabsorption. The segment also reabsorbs Ca2+ through apical Ca2+ channel (transient receptor potential vanniloid type 5, TRPV5) and basolateral Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX1) and Ca2+ pump. In the DCT cell, Ca2+ is buffered and transported by parvalbumin (Pvlb; DCT1) or calbindin-2 (Calb; DCT2). PMCA1b, plasma membrane Ca2+-ATPase 1b.