Fig. 12.
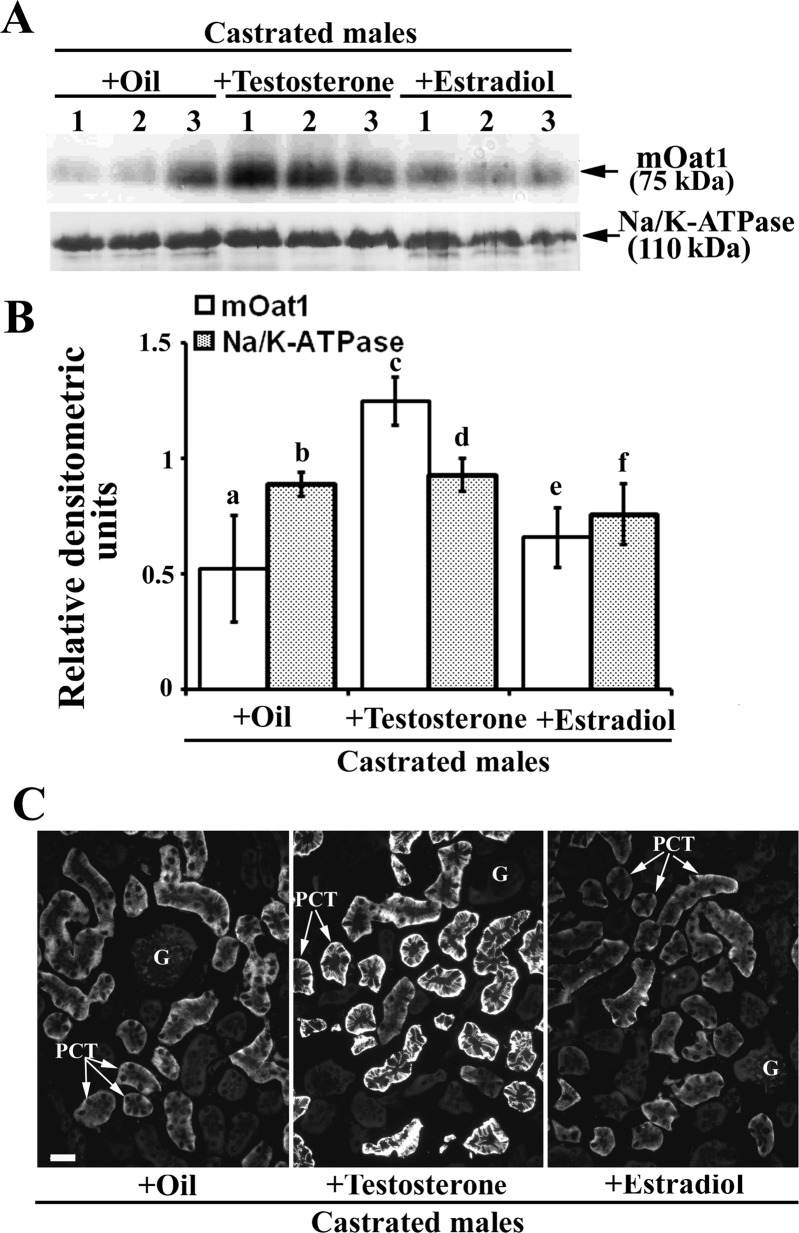
Expression of the renal mOat1 protein in adult castrated male mice–effects of treatment with sex hormones; Western blot (A and B) and immunocytochemical (C) analysis. A: Western blot of the renal TCM with rOat1-Ab and Na-K-ATPase-Ab in castrated males treated with oil, testosterone and estradiol. B: densitometric evaluation of the same bands. Compared with the oil-treated castrated mice, testosterone strongly increased (∼2.4-fold), whereas estradiol did not change, the expression of the mOat1-related protein band of ∼75 kDa. The relative density of the Na-K-ATPase protein band of 110 kDa remained unaffected by either sex hormone. Each lane contained 80 μg of protein. Each bar is the means ± SE of the data from 3 independent TCM preparations. Statistics: a vs. c and c vs. e, P < 0.05; other relations, NS. C: rOat1-Ab-related immunostaining in cryosections of formalin-fixed kidneys from castrated males treated with oil, testosterone or estradiol. Intensity of the mOat1-related fluorescence staining completely matched the Western blotting data; compared with the oil-treated castrates, testosterone treatment markedly increased the staining intensity of the BLM in PCT, whereas the estradiol treatment had not effect. Immunocytochemical data represent findings in 3 animals in each experimental group. Bar = 20 μm.