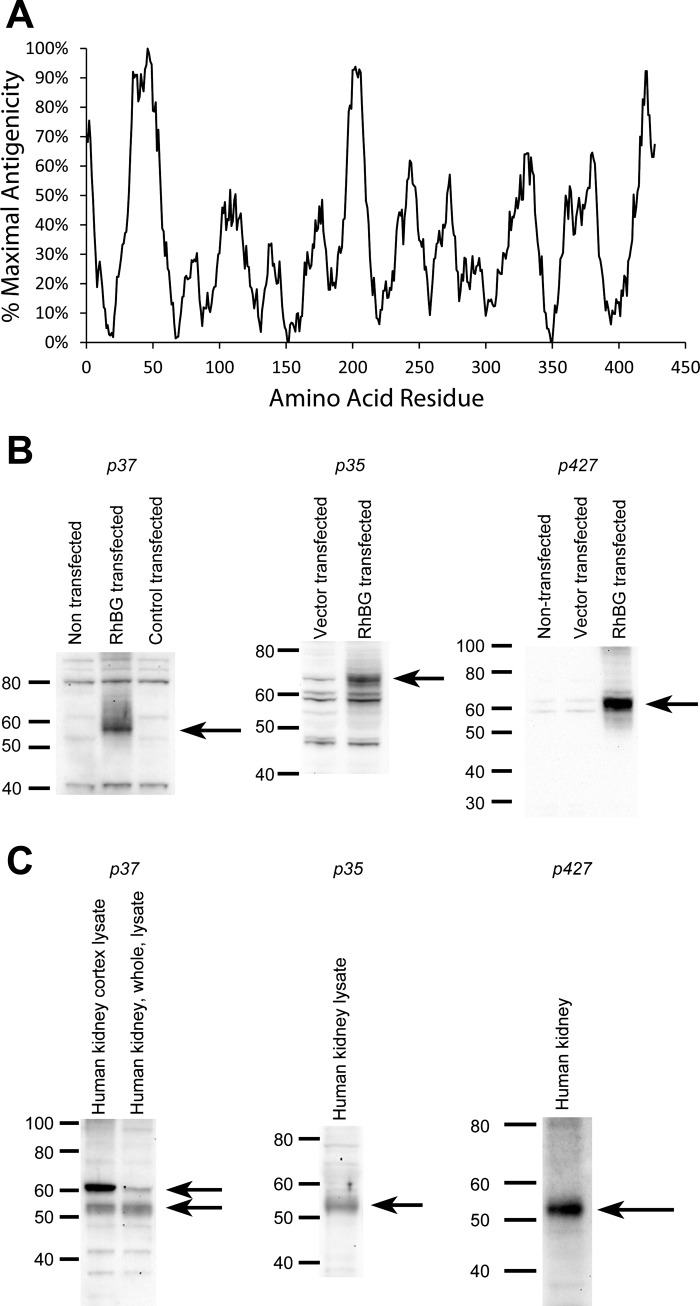
Fig. 2.
Prediction of antigenicity of 15 amino acid residue peptides along the human RhBG protein. A: use of NHLBI AbDesigner software (25) to predict antigenicity of 15 amino acid residue peptides, beginning at residue 1 and continuing through residue 427. Relative antigenicity is shown, with maximal antigenicity plotted as 100%. B: characterization of anti-peptide RhBG antibodies. B, left: immunoblot of CV-1 cells either nontransfected, transfected with c-RhBG, or transfected with control vector and immunoblotted with anti-p37 antibody. Arrow shows detection of ∼57-kDa RhBG protein. Bands at ∼41 and 80 kDa are either nonspecific or may represent detection of endogenous Rhbg protein in monomeric and dimeric nonglycosylated forms. B, middle: immunoblot of CV-1 cells transfected either with control vector or with c-GFP-RhBG vector and immunoblotted with p35 antibody. Arrow shows detection of ∼70-kDa GFP-RhBG protein. The increase in apparent molecular weight likely reflects differences in mobility related to inclusion of GFP in protein. B, right: protein from nontransfected HEK cells or from HEK cells transfected either with vector or with c-RhBG. Immunoblot analysis shows expression of ∼61-kDa RhBG protein. The slight difference in molecular weight compared with A may reflect differences in glycosylation in different cell types. C, left: immunoblot analysis of human kidney proteins with antibody p37, and it demonstrates identification of ∼54- and 61-kDa bands. C, middle: immunoblot analysis with p35 antibody, and it demonstrates identification of ∼54-kDa protein. C, right: immunoblot analysis using p427 antibody, and it demonstrates expression of 55-kDa protein. Slight variations likely reflect interexperimental variations in mobility.