Fig. 3.
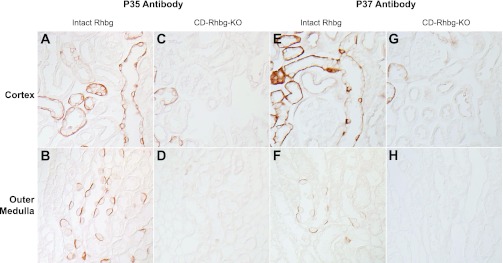
Immunohistochemistry in kidney tissues in mice with intact and collecting duct (CD)-specific Rhbg deletion (CD-Rhbg-KO). A and B: immunohistochemistry of the cortex and outer medulla of mouse kidney with intact Rhbg expression using antibody p35. Basolateral Rhbg immunolabel is easily evident. C and D: similar studies using antibody p35, except performed in mouse kidney with CD-Rhbg-KO. No significant immunolabel is present in the CD; minimal residual immunolabel is present in the connecting segment (CNT) and distal convoluted tubule (DCT), segments that retain a low level of Rhbg expression in this genotype (unpublished observations). E and F: immunohistochemistry of mouse kidney with intact Rhbg expression using antibody p37 in the cortex and outer medulla. Again, basolateral Rhbg immunolabel is easily evident. G and H: similar studies using antibody p37, except performed in mouse kidney with CD-Rhbg-KO. No significant immunolabel is present in the CD; minimal residual immunolabel is present in the CNT and DCT, segments that retain a low level of Rhbg expression in this genotype. Mice with intact Rhbg expression expressed floxed Rhbg alleles and did not express Cre-recombinase. Mice with CD-Rhbg-KO expressed floxed Rhbg alleles and expressed Cre-recombinase under control of Ksp-cadherin promoter. All tissues were treated with peptide:N-glycosidase F (PNGase F) as described in methods.
