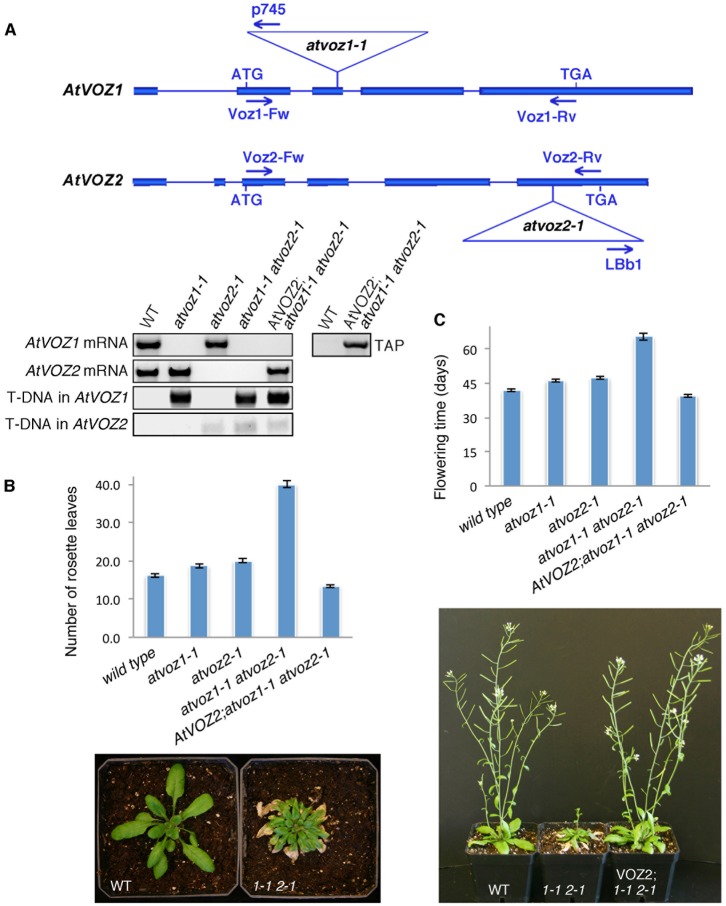
Fig. 1. AtVOZ proteins are activators of floral transition in Arabidopsis.
(A) Top: diagrammatic representation of AtVOZ1 and AtVOZ2 genes. Exons, blue rectangles; introns, blue lines. T-DNA insertion sites in atvoz mutants are indicated by triangles. Bottom: genotyping of atvoz1-1 and atvoz2-1 single mutants, atvoz1-1 atvoz2-1 double mutant, and AtVOZ2; atvoz1-1 atvoz2-1 complemented line with gene-specific or T-DNA-specific primers indicated in the above diagram. TAP-specific primer was used to detect expression of CTAP-AtVOZ2 in the complemented line. (B) Top: number of rosette leaves at bolting for WT, atvoz single and double mutants and complemented line under LD conditions. Mean values±s.e.m. are shown. Bottom: phenotypic comparison of WT and atvoz1-1 atvoz2-1 (1-1 2-1) plants at the beginning of bolting. Increased leaf number and extensive senescence is seen for atvoz1-1 atvoz2-1. (C) Top: flowering time, measured as number of days to opening of the first flower, for WT, atvoz single and double mutants and complemented line under LD conditions. Mean values±s.e.m. are shown. Bottom: phenotypic comparison of 9-week-old WT, atvoz1-1 atvoz2-1 (1-1 2-1) and complemented (VOZ2;1-1 2-1) plants at the time of opening of the first atvoz1-1 atvoz2-1 flower.