Fig. 5.
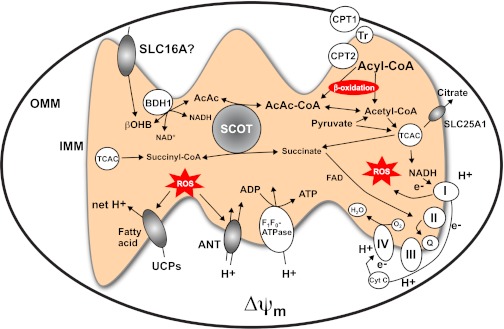
Diverse roles of CoA transferase in mitochondrial function. βOHB and AcAc cross the plasma membrane via solute ligand carrier protein (SLC) 16A (SLC16A) family members and may employ these or other transporters to enter the mitochondrial matrix. Within the mitochondria, d-βOHB is oxidized to AcAc by the inner-membrane bound and phosphatidylcholine-dependent BDH1. CoA transferase (SCOT) catalyzes a near equilibrium reaction through which CoA is exchanged between succinate and AcAc. Oxidation of ketone bodies occurs by mass action and may diminish reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation, compared with oxidation of fatty acids. See text for details. ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ANT, adenine nucleotide transporter; CPT, carnitine palmitoyltransferase; Cyt C, cytochrome c; e−, electron; H+, hydrogen ion; I, II, II, IV, complexes I-IV of the electron transport chain, respectively; IMM, inner mitochondrial membrane; OMM, outer mitochondrial membrane; Q, ubiquinone; Δψm, electrochemical potential across the inner mitochondrial membrane; Tr, translocase; UCPs, uncoupling proteins; FAD, flavin adenine dinucleotide.
