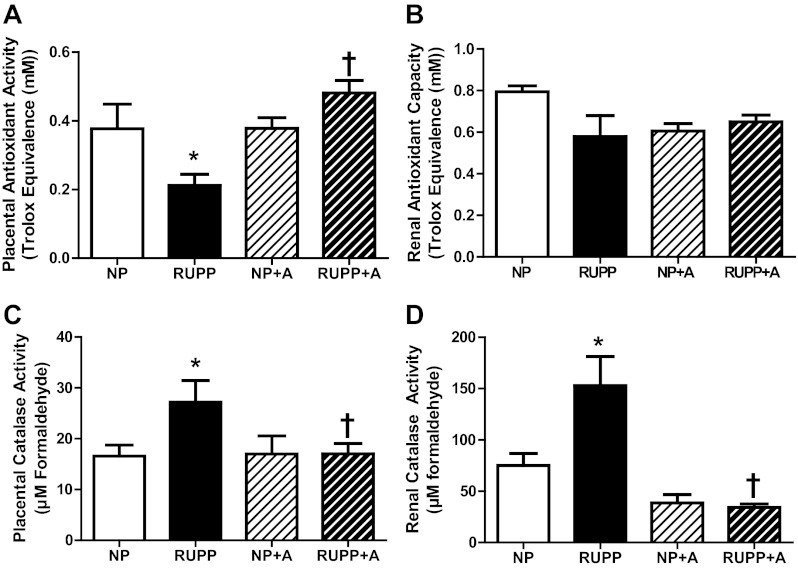
Fig. 4.
Markers of oxidative stress in the RUPP rat were reduced by chronic AICAR administration. A: trolox-equivalent antioxidant capacity (TEAC) levels were decreased in the RUPP placenta compared with the NP (P < 0.05) and AICAR (50 mg/kg twice a day) treatment obviated the decrease in the RUPP + A. B: renal TEAC levels were unaffected by AICAR treatment. C: placental catalase activity (measured by formaldehyde production) was increased (P < 0.05) in the RUPP vs. NP and decreased (P < 0.05) in RUPP + A with respect to RUPP. D: renal catalase activity was increased (P < 0.05) in the RUPP vs. NP and decreased (P < 0.05) in RUPP + A with respect to RUPP. *P < 0.05, different from NP; †P < 0.05, different from RUPP. Data presented as means ± SE; n = 8 RUPP, 8 NP, 6 NP + A, and 8 RUPP + A.