Figure 3. Consequences of Survival Circuit Activation.
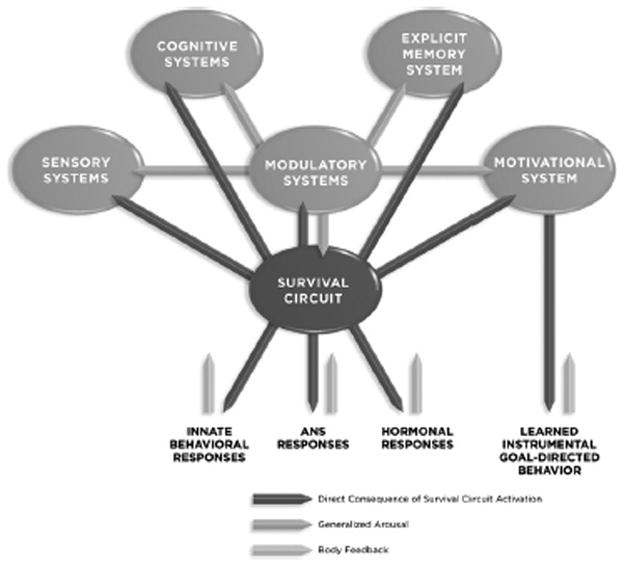
When a survival circuit trigger activates a survival circuit, a number of consequences follow. (1) Innate behavioral responses are potentially activated, as well as autonomic nervous system (ANS) responses and hormonal responses. These each generate feedback to the brain. (2) Neuromodulator systems are activated and begin to regulate excitability and neurotransmission throughout the brain. (3) Goal directed instrumental behavior is initiated by the motivation system. (4) Sensory, cognitive, and explicit memory systems are also affected, leading to enhanced attention to relevant stimuli and the formation of new explicit memories (memories formed by the hippocampus and related cortical areas) and implicit memories (memories formed within the survival circuit).
