Fig. 3.
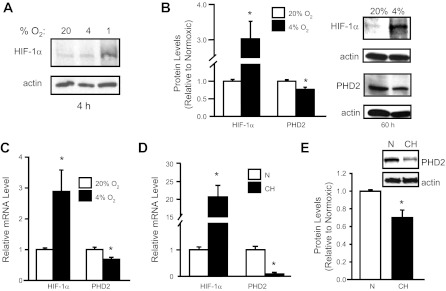
Hypoxia alters HIF-1α and PHD2 expression in PASMCs. PASMCs were exposed to a short (4 h) or long (60 h) duration of hypoxia (1 or 4% O2) ex vivo or pulmonary arteries were isolated from rats exposed to ambient hypoxia [3 wk; inspired O2 fraction (FiO2) = 10% O2]. Protein and mRNA levels were measured via immunoblot and real-time RT-PCR assays, respectively. A: HIF-1α protein in PASMCs after short-duration ex vivo hypoxic exposure at different O2 levels. B: HIF-1α and PHD2 protein expression in PASMCs after ex vivo exposure to prolonged, moderate hypoxia (60 h; 4% O2). Bar graphs show mean ± SE from 4 separate experiments. C: HIF-1α and PHD2 mRNA levels in PASMCs exposed to ex vivo hypoxia (60 h; 4% O2) relative to levels measured in nonhypoxic cells (n = 4). *P < 0.05 vs. 20% O2. D: HIF-1α and PHD2 mRNA levels in endothelium-denuded intralobar pulmonary arteries from rats exposed to chronic hypoxia (CH) relative to levels in pulmonary arteries from normoxic (N) rats (n = 3). *P < 0.05 vs. N. E: PHD2 protein expression in intralobar pulmonary arteries from N and CH rats. For all bar graphs, mean ± SE values are shown. Data are normalized to cyclophilin B or actin for mRNA and protein, respectively, and expressed relative to normoxic. *P < 0.05 vs. N.
