Fig. 3.
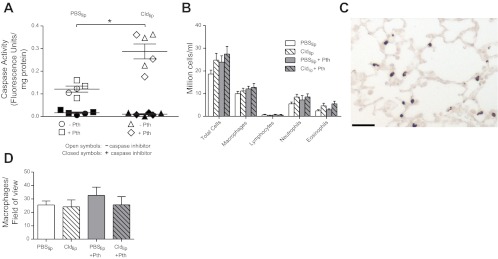
Pretreatment with Cldlip increased caspase-3 activity in alveolar macrophages but did not deplete the number of alveolar or interstitial macrophages. A: caspase-3 activity was measured in alveolar macrophages using a fluorogenic substrate and normalized to protein concentration. Pretreatment with Cldlip (n = 6) significantly increased caspase-3 activity in alveolar macrophages isolated from control or parathion-treated guinea pigs relative to alveolar macrophages isolated from guinea pigs that received PBSlip (n = 5). To confirm that the fluorescent signal was due to caspase activity, fluorescence was also quantified in duplicate samples to which the caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO had been added. B: the number of macrophages and other inflammatory cells in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) was not changed by treatment with either parathion or Cldlip (n = 7–9). As shown in a representative photomicrograph from a guinea pig that received Cldlip (C), interstitial lung macrophages were identified by calprotectin immunoreactivity (bar = 100 μm). D: the number of interstitial macrophages per unit area was not changed by either parathion or Cldlip treatment (n = 4–7). Data are presented as means ± SE (*P ≤ 0.05).
