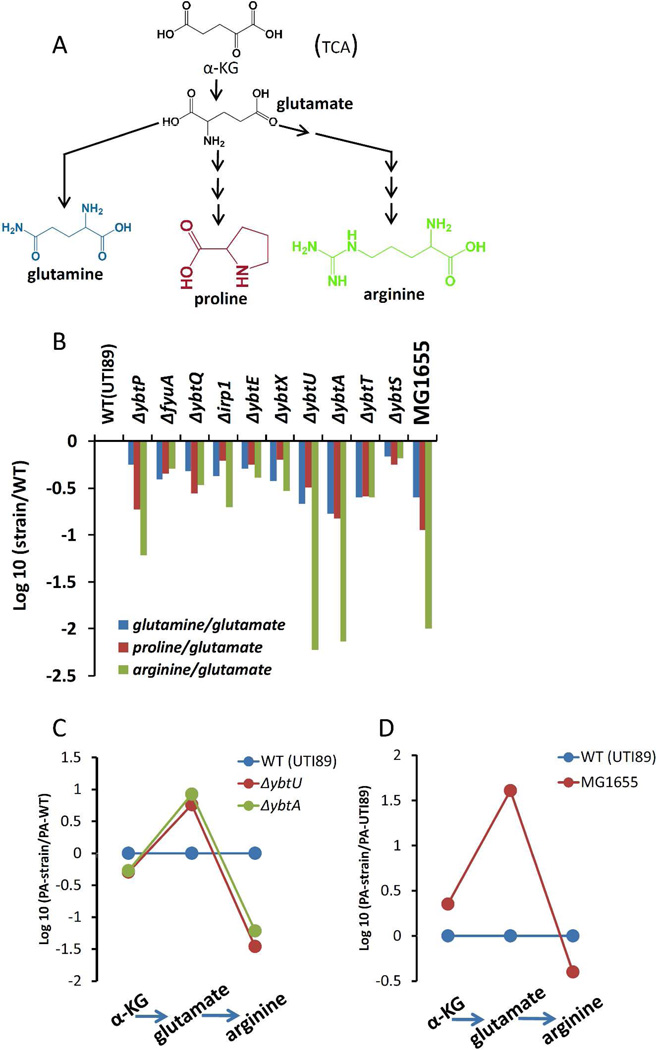
Figure 7. ybtU and ybtA mutants exhibit metabolite levels consistent with selectively diminished arginine biosynthesis.
(A) The glutamate family of amino acids glutamine, proline, and arginine are synthesized from glutamate. (B) Among glutamate family amino acids, the arginine/glutamate ratio (product/precursor ratio expressed on a log scale) is reduced by over 100-fold in ybtA and ybtU mutants relative to other HPI mutants and to a similar degree in K12 E.coli strain MG1655, which lacks Yersinia HPI genes. Glutamine and proline are much less markedly affected. (C) Relative (compared to wild type UTI89) metabolite levels along the arginine biosynthesis pathways of UTI89ΔybtU and UT89ΔybtA. Accumulation of glutamate (substrate) levels together with diminished arginine (product) levels are consistent with a relative metabolic block in arginine biosynthesis. Relatively stable levels of alpha-ketoglutarate (α-KG), from which glutamate is synthesized, likely reflect its carefully regulated steady state levels as a TCA cycle intermediate. (D) Arginine biosynthesis pathway metabolites in MG1655 exhibit shifts in glutamate and arginine levels comparable to those observed in UTI89ΔybtU and UTI89ΔybtA.