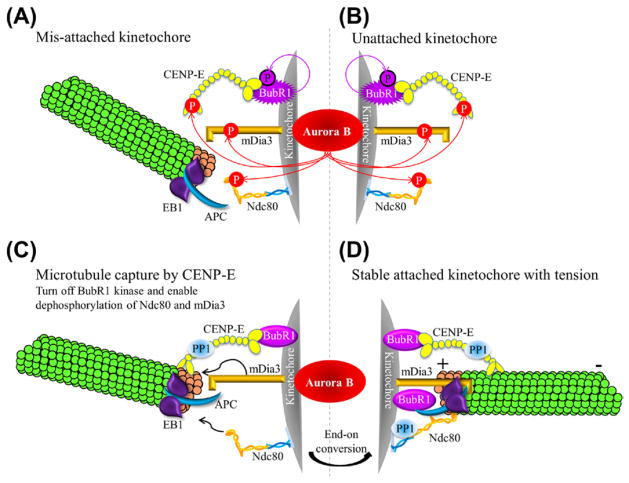
Figure 6.3. A model for establishing proper stable kinetochore-microtubule attachment.
(A and B) Mis-attached (A) or unattached (B) kinetochores have Aurora B-mediated phosphorylation of the KMN network (represented by Ndc80 complex in the cartoon), CENP-E, and the formin mDia3, which causes destabilization of improperly attached kinetochore microtubules. (C) Upon spindle microtubule capture, CENP-E can turn off the kinase activity and auto-phosphorylation of BubR1 and recruit PP1. Both activities are essential to reduce Aurora B-mediated phosphorylation on kinetochore-associated substrates. These coordinated events enable the Ndc80 and mDia3 to bind to microtubules. (D) After converting into end-on attachment to produce tension, the inter kinetochore stretch separates the inner centromeric Aurora B from outer kinetochore substrates, resulting in stable kinetochore-microtubule attachment. (For color version of this figure, the reader is referred to the online version of this book.)