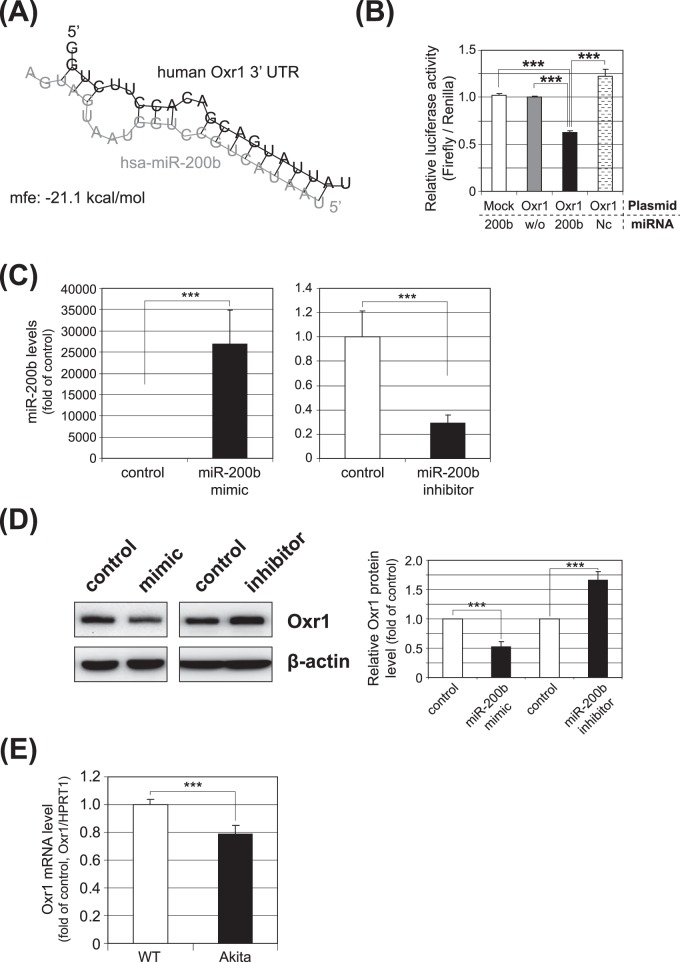
Figure 3.
Validation of Oxr1 as a target gene of miRNA-200b. (A) The predicted secondary structure of the miR-200b binding site in the 3′UTR of human Oxr1 is shown; minimum free energy (mfe) is calculated and shown. (B) Luciferase reporter vectors containing the miR-200b target sequence of Oxr1 (Oxr1), or the same vector without the target sequence (Mock) were cotransfected with miR-200b mimic (200b), without miRNA (w/o), or with mismatched oligos (Nc, negative control) into ARPE-19 cells for 36 hours, and a dual luciferase assay subsequently was conducted. The luciferase activity was decreased significantly by cotransfection with the miR-200b mimic (***P < 0.001). (C) qRT-PCR analysis of miR-200b expression following transfection of the miR-200b mimic (left) or the miR-200b inhibitor (right) in MIO-M1 cells. The results are presented as fold change over the control (mean ± SEM, n = 6; ***P < 0.001). (D) Regulation of Oxr1 expression by miR-200b mimic and its inhibitor. Western blot analyses of Oxr1 were conducted 48 hours after transfection of miR-200b mimic or its inhibitor (left). Oxr1 protein levels were semiquantified by densitometry (right, mean ± SEM, n = 3, ***P < 0.001). (E) Oxr1 mRNA levels in the retina of Akita mice and Wt mice were analyzed by qRT-PCR (mean ± SEM, n = 7, ***P < 0.001).