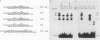Abstract
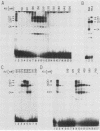
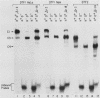
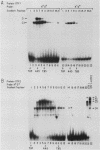
Immunoglobulin heavy-chain genes contain two conserved sequence elements 5' to the site of transcription initiation: the octamer ATGCAAAT and the heptamer CTCATGA. Both of these elements are required for normal cell-specific promoter function. The present study demonstrates that both the ubiquitous and lymphoid-cell-specific octamer transcription factors (OTF-1 and OTF-2, respectively) interact specifically with each of the two conserved sequence elements, forming either homo- or heterodimeric complexes. This was surprising, since the heptamer and octamer sequence motifs bear no obvious similarity to each other. Binding of either factor to the octamer element occurred independently. However, OTF interaction with the heptamer sequence appeared to require the presence of an intact octamer motif and occurred with a spacing of either 2 or 14 base pairs between the two elements, suggesting coordinate binding resulting from protein-protein interactions. The degeneracy in sequences recognized by the OTFs may be important in widening the range over which gene expression can be modulated and in establishing cell type specificity.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ballard D. W., Bothwell A. Mutational analysis of the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9626–9630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Rice D., Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Two regulatory elements for immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreyfus M., Doyen N., Rougeon F. The conserved decanucleotide from the immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter induces a very high transcriptional activity in B-cells when introduced into an heterologous promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1685–1690. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eaton S., Calame K. Multiple DNA sequence elements are necessary for the function of an immunoglobulin heavy chain promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7634–7638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkner F. G., Zachau H. G. Correct transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa gene requires an upstream fragment containing conserved sequence elements. Nature. 1984 Jul 5;310(5972):71–74. doi: 10.1038/310071a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster J., Stafford J., Queen C. An immunoglobulin promoter displays cell-type specificity independently of the enhancer. 1985 May 30-Jun 5Nature. 315(6018):423–425. doi: 10.1038/315423a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Roeder R. G. A herpesvirus trans-activating protein interacts with transcription factor OTF-1 and other cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6347–6351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawakami K., Scheidereit C., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human immunoglobulin-enhancer-binding protein (NF-kappa B) that activates transcription from a human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knapp M. R., Liu C. P., Newell N., Ward R. B., Tucker P. W., Strober S., Blattner F. Simultaneous expression of immunoglobulin mu and delta heavy chains by a cloned B-cell lymphoma: a single copy of the VH gene is shared by two adjacent CH genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2996–3000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaBella F., Sive H. L., Roeder R. G., Heintz N. Cell-cycle regulation of a human histone H2b gene is mediated by the H2b subtype-specific consensus element. Genes Dev. 1988 Jan;2(1):32–39. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.1.32. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Interaction of cell-type-specific nuclear proteins with immunoglobulin VH promoter region sequences. Nature. 1986 Oct 9;323(6088):548–551. doi: 10.1038/323548a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Protein-nucleotide contacts in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3851–3855. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landolfi N. F., Yin X. M., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. A conserved heptamer upstream of the IgH promoter region octamer can be the site of a coordinate protein-DNA interaction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jun 24;16(12):5503–5514. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.12.5503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason J. O., Williams G. T., Neuberger M. S. Transcription cell type specificity is conferred by an immunoglobulin VH gene promoter that includes a functional consensus sequence. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):479–487. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80021-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizushima-Sugano J., Roeder R. G. Cell-type-specific transcription of an immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8511–8515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Fletcher C., Burrow C. R., Heintz N., Roeder R. G., Kelly T. J. Transcription factor OTF-1 is functionally identical to the DNA replication factor NF-III. Science. 1988 Sep 2;241(4870):1210–1213. doi: 10.1126/science.3413485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J. Purification and characterization of nuclear factor III (origin recognition protein C), a sequence-specific DNA binding protein required for efficient initiation of adenovirus DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):931–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Schaffner W. Cell-type preference of immunoglobulin kappa and lambda gene promoters. EMBO J. 1985 Nov;4(11):2831–2838. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van Miltenburg R. T., van der Vliet P. C. Promoter and enhancer elements containing a conserved sequence motif are recognized by nuclear factor III, a protein stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3771–3778. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02712.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Heguy A., Roeder R. G. Identification and purification of a human lymphoid-specific octamer-binding protein (OTF-2) that activates transcription of an immunoglobulin promoter in vitro. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):783–793. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu G., Springer E. A., Huang H. V., Hood L. E., Crews S. T. Structure of the T15 VH gene subfamily: identification of immunoglobulin gene promotor homologies. J Immunol. 1987 Jun 15;138(12):4466–4471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staudt L. M., Singh H., Sen R., Wirth T., Sharp P. A., Baltimore D. A lymphoid-specific protein binding to the octamer motif of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Oct 16;323(6089):640–643. doi: 10.1038/323640a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger J., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Distinct factors bind to apparently homologous sequences in the immunoglobulin heavy-chain enhancer. 1986 Aug 28-Sep 3Nature. 322(6082):846–848. doi: 10.1038/322846a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth T., Staudt L., Baltimore D. An octamer oligonucleotide upstream of a TATA motif is sufficient for lymphoid-specific promoter activity. Nature. 1987 Sep 10;329(6135):174–178. doi: 10.1038/329174a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C., Wilson S., Walker B., Dawid I., Paisley T., Zimarino V., Ueda H. Purification and properties of Drosophila heat shock activator protein. Science. 1987 Nov 27;238(4831):1247–1253. doi: 10.1126/science.3685975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]