Figure 1.
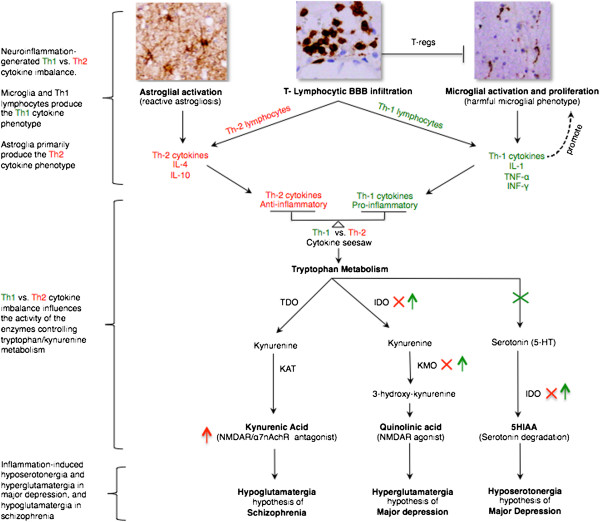
Influence of the ‘Th1-Th2 cytokine seesaw’ generated by glial cells and T lymphocytes on tryptophan/kynurenine metabolism-mediated serotonergic and glutamatergic abnormalities in major depressive disorder and schizophrenia. Influence of the ’Th1-Th2 seesaw’ generated by glial cells and T lymphocytes (first of three bracketed sections) on the enzymes controlling tryptophan/kynurenine metabolism (second of three bracketed sections) leading to serotonergic and glutamatergic abnormalities in major depressive disorder and schizophrenia (third of three bracketed sections). Microglial and astroglial IDO is the rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing the conversion of tryptophan to KYN and serotonin to 5HTT. KMO, which is solely expressed by microglia, is the rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing the conversion of KYN to 3-OH-KYN. TDO, which is solely expressed by astroglia, is the rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing the conversion of tryptophan to KYN. KAT, expressed primarily in astroglial processes, is the rate-limiting enzyme catalyzing the conversion of KYN to KYNA. The microglial enzymes IDO and KMO are upregulated by Th1 cytokines and downregulated by Th2 cytokines. An imbalance of the ‘Th1-Th2 seesaw’ shifts kynurenine catabolism either towards microglial quinolinic acid (NMDA agonist) as in major depressive disorder, or towards astroglial kynurenic acid (NMDA antagonist) as in schizophrenia. 5HIAA, 5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid; α7nAchR, alpha 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptors; BBB, blood–brain barrier; IDO, indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase; IL, interleukin; IFN-γ, interferon gamma; KAT, kynurenine aminotransferase; KMO, kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; KYN, kynurenine; KYNA, kynurenic acid; NMDAR, N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor alpha; T regs, CD4+CD25+FOXP3+ T regulatory cells; TDO, tryptophan-2,3-dioxygenase; Th, T-helper.
