Figure 4.
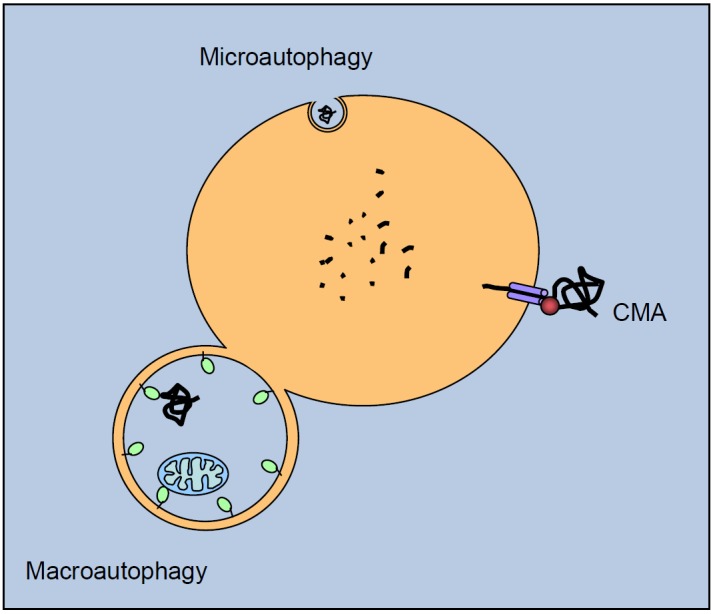
Autophagic pathways. Cytosolic proteins are degraded in the lysosomal lumen (yellow) through three different autophagic mechanisms. In microautophagy, the lysosomal membrane invaginates to engulf a small portion of cytosol with its contents. In chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA), a targeting motif in the substrate proteins is recognized by a cytosolic chaperone (red sphere) that delivers it to a lysosomal receptor. This receptor multimerizes to form a translocation complex that mediates the translocation of the substrate protein into the lumen of the lysosome. In macroautophagy, a double membrane vesicle sequesters cargo proteins and a whole region of the cytosol, and then fuses with the lysosome for cargo delivering. Once in the lysosomal lumen, proteins as well as other macromolecules are rapidly degraded by multiple enzymes, including cathepsins.
