Table 2.
Coefficients and exponents for flow–area and flow–length scaling power laws in epicardial coronary arterial trees of high-fat diet and control groups. The values were mean±s.d. (averaged over arterial trees). One-way ANOVA was used to compare coefficients between the high-fat diet and control groups.
| scaling power laws |
high-fat diet (n = 6) | control (n = 6) | per cent difference (%) | p-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| least-squares fit of both K0 and X values (two-parameter model) | |||||
flow–area scaling law (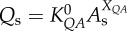 ) ) |
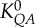 |
4.02±2.75 | 5.62±1.16 | −28.4 | =0.21 |
| XQA | 1.05±0.24 | 1.16±0.09 | −9.7 | =0.29 | |
| R2 | 0.66±0.07 | 0.94±0.01 | |||
flow–length scaling law (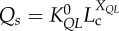 ) ) |
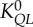 |
2.28±0.35 (×10–2) | 3.17±0.67 (×10–2) | −28.0 | =0.14 |
| XQL | 0.90±0.07 | 0.79±0.06 | 13.5 | =0.05 | |
| R2 | 0.91±0.08 | 0.91±0.02 | |||
| least-squares fit of K values with X equal to theoretical values (one-parameter model) | |||||
flow–area scaling law (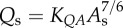 ) ) |
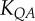 |
4.59±0.56 | 6.00±0.91 | −23.5 | =0.09 |
| R2 | 0.66±0.07 | 0.94±0.01 | |||
| flow–length scaling law (Qs = KQLLc) | KQL | 2.03±0.34 (×10–2) | 2.58±0.56 (×10–2) | −21.2 | =0.25 |
| R2 | 0.91±0.08 | 0.91±0.02 | |||
