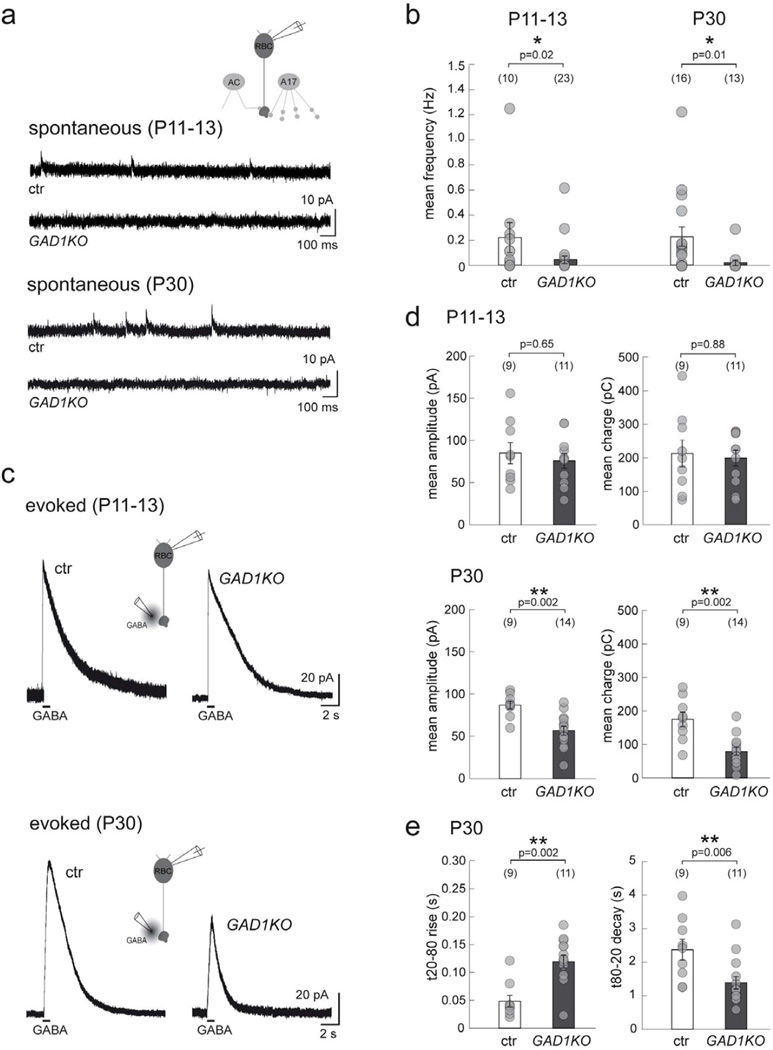
Figure 4. Spontaneous and GABA-evoked currents of RBCs in GAD1KO retina.
(a) Spontaneous GABAergic IPSCs at RBC axon terminals recorded from GAD1KO and littermate control (ctr) at P11–13 and P30. (b) Scatter plots show that the mean frequency of these sIPSCs are reduced in GAD1KO as compared to ctr. (c) Puffs of GABA evoke similar chloride-mediated outward currents in RBCs from ctr and GAD1KO at P11–13, which are markedly reduced for GAD1KO RBCs at P30. (d) Quantification reveals a significant reduction for both the mean peak amplitude and charge of GABA-evoked currents from GAD1KO RBCs at P30. (e) In addition, the rise time for the P30 evoked response from GAD1KO RBCs is longer while the decay is faster as compared to control. Numbers in brackets in b, d, and e represents number of cells. Asterisks mark significant difference. Error bars represent S.E.M.