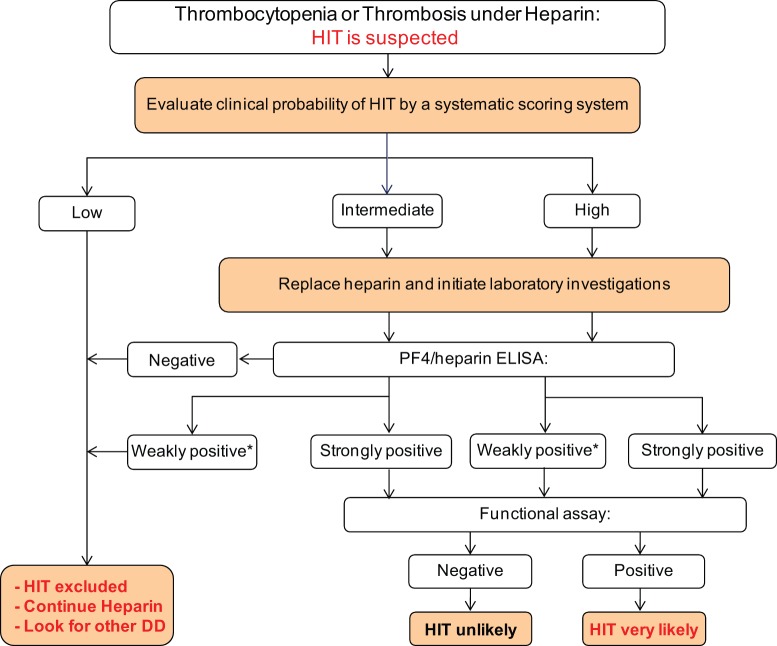
Figure 1.
A suggested approach to diagnosis and initial management of patients with suspected HIT.This approach to the diagnosis and initial management of patients with suspected HIT is based on clinical assessment supported by complementary laboratory investigations. Results of Immunoassays can be devided into neagtive, weakly positive (OD < 1.0) and strong positive (OD>1.0). The decision whether weakly positive results need to be further verfied using functional assays or not depends on the clinical probabilty. As indeterminate results may be occasionally obtained using laboratory tests, re-evaluating the clinical probability of HIT in an individual patient may be helpful to overcome some diagnostic uncertainty.