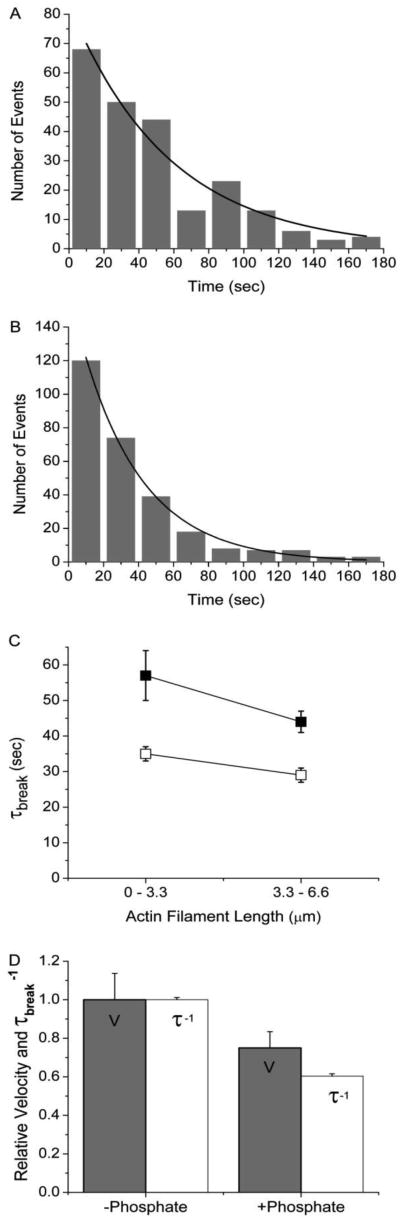
Figure 5.
[Pi] dependence of actin sliding velocities and the rate of actin filament breaking. (A) Actin filament break times, τbreak, were measured in the presence of 30 mM Pi at 30 μM ATP for filaments < 3.3 μm and plotted in a histogram (n = 224). The data were fitted to a single exponential (solid line) to obtain the actin filament lifetime (τbreak). (B) Actin filament break times, τbreak, were measured in the presence 30 μM ATP with no added Pi for filaments < 3.3 μm and plotted in a histogram (n = 279). The data were fitted with a single exponential (solid line) to obtain the average time to break (τbreak). (C) Values for the actin filament lifetime (τbreak) obtained with (dark squares) and without (white squares) added Pi at 30 μM ATP are plotted both for actin filament lengths < 3.3 μm and for actin filament lengths between 3.3 and 6.6 μm. (D) For all actin filament lengths, mean actin sliding velocities (grey bars), normalized to 1.8 μm·sec−1, and the rates of actin breaking (white bars), normalized to 0.029 sec−1, obtained in the presence and absence of 30 mM Pi at 30 μM ATP are plotted, showing that the inhibition of V by Pi corresponds to a decrease in interhead forces.