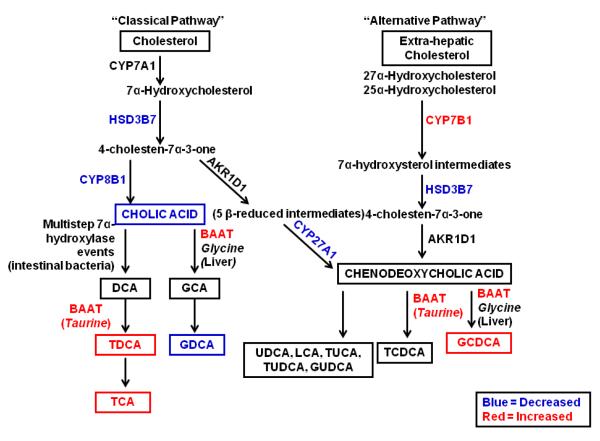
Figure 6. Bile Acid Synthesis in Human NASH.
A simplified schematic of the hepatic classical and alternative pathways of BA synthesis in human NASH is provided. Increased levels of metabolites (TCA, TDCA, GCDCA and taurine) are shown in red. Gene expression increases of metabolizing enzymes (BAAT, CYP7B1) are also shown in red. Decreased metabolite levels (CA, GDCA) and enzyme gene expression (CYP27A1, CYP8B1, and HSD3B7) is represented in blue. Unchanged metabolites (CDCA/DCA, GUDCA, TUCA, TUDCA, GCA) and enzymes (CYP7A1, AKR1D1) are shown in black. Note: Not every enzymatic step in BA synthesis and systemic enterohepatic recycling of BAs is shown in this schematic. This pathway is adapted and modified from (Beilke et al., 2009) and (Thomas et al., 2008).