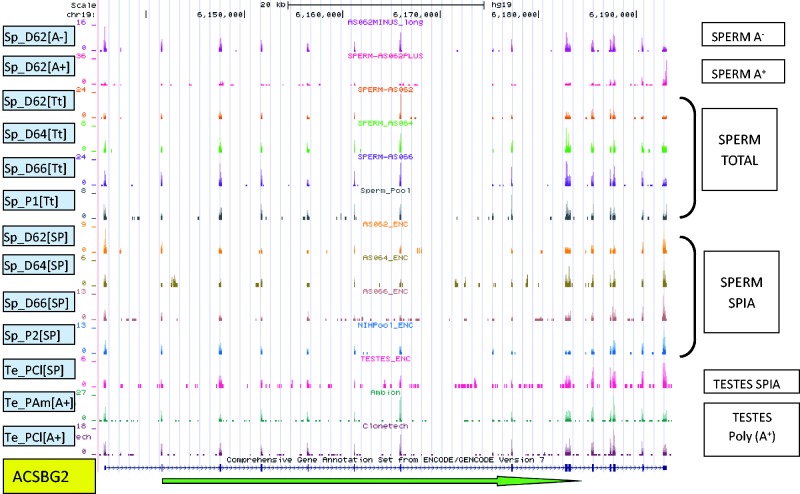
Figure 1.
The distribution of sequencing reads across ACSBG2 in all libraries. The green arrow indicates transcript orientation. The number of reads corresponding to each read start at each base position is represented on the vertical axis. The scale for each sample is based on maximum read count within the displayed region. Four Total Sperm samples—Sp_D62[Tt], Sp_D64[Tt], Sp_D66[Tt] (individual donors) and Sp_P1[Tt] (mixed pool of three random donors)—were not subject to any of the commonly used RNA-selection methods. Sample D62 was additionally separated into Poly(A+) (Sp_D62[A+]) and Poly(A-) (Sp_D62[A−]) fractions by oligo(dT) selection. Commercially obtained pooled testes RNA—Te_PAm[A+] (Applied Biosystems/Ambion, Austin, TX, USA, Lot 054P010702031A) and Te_PCl[A+] (ClonTech, Mountain View, CA, USA, Lot 3090051)—were subject to Poly(A+) selection. Sequences from Single Primer Isothermal Amplification (SPIA—Nugen Ovation Nugen Inc., San Carlos, CA, USA) (Sp_D62[SP], Sp_D64[SP], Sp_D66[SP]), a single pooled sperm sample (Sp_P2[SP]) and a single pooled testes (Te_PAm[SP]) prepared libraries are compared.