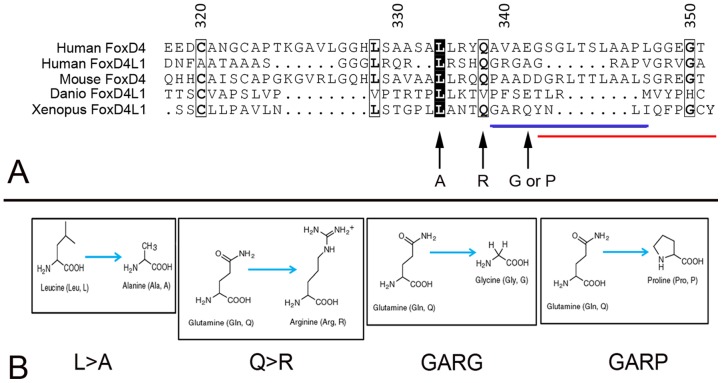
Figure 3. Conserved amino acids in the extreme C-terminus of FoxD4/FoxD4L1 proteins.
(A) CLUSTALW alignment [64], viewed in ESPript [65], of the extreme C-terminal region of human FoxD4 (UniProtKB/Swiss Prot accession number Q12950), human FoxD4L1 (Q9NU39), mouse FoxD4 (Q60688), Danio FoxD4L1 (O73784) and Xenopus laevis FoxD4L1 (Q9PRJ8). The black boxes highlight identical amino acids, the light boxes highlight conserved amino acids and the bold letters indicate identical amino acids within a conserved region. The blue line denotes the amino acids in the Xenopus sequence predicted to form an α-helix, and the red line denotes Motif 6 (Fig. 1A). Arrows denote amino acid substitutions in the C-terminal mutants used in this study (L>A; Q>R; GARQ>GARG; GARQ>GARP). (B) Amino acid changes made in the C-terminal mutants used in this study.