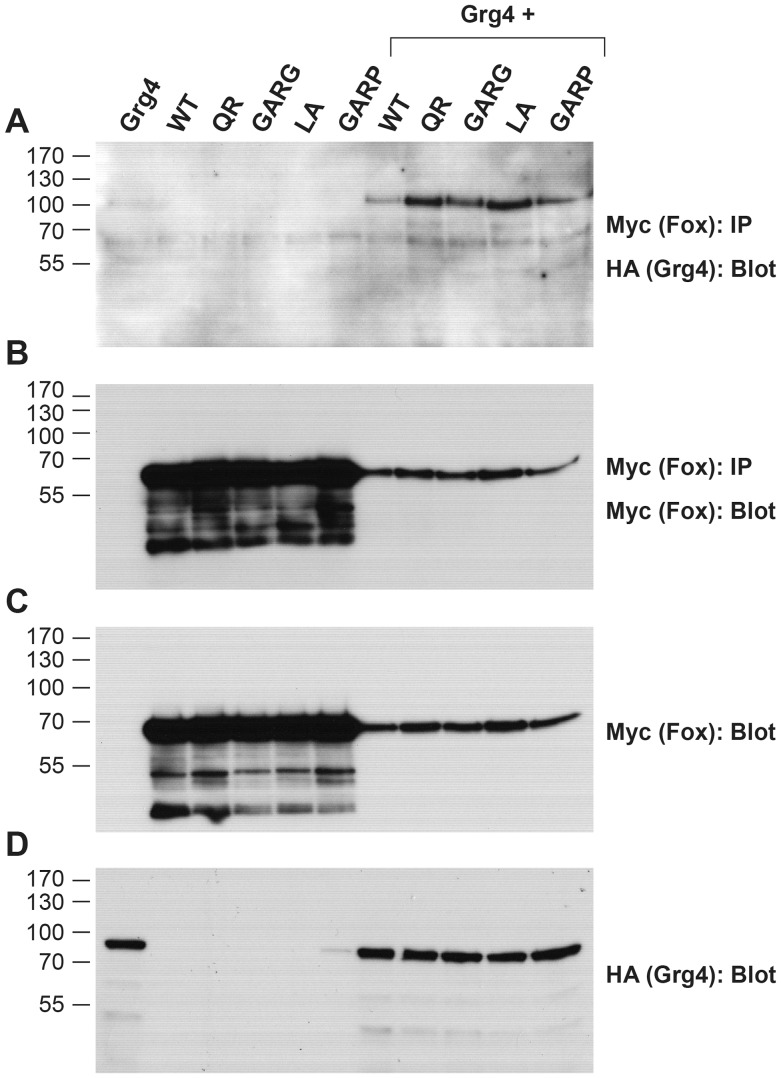
Figure 7. Grg4 binds to the FoxD4L1 C-term mutants.
(A–D) Myc-tagged versions of wild-type (WT), as well as mutants harboring amino acid substitutions downstream of the Eh-1 domain (QR, GARG, LA, GARP) in FoxD4L1 were expressed in Xenopus oocytes along with HA-tagged wild-type Xenopus Grg4. Co-immunoprecipitation (IP) and Western blot (WB) analyses of oocyte lysates expressing HA- and Myc-tagged constructs are indicated. (A) All four constructs bind with Grg4. The control panels (B–D) show that the IPs contain similar levels of FoxD4L1 wild-type and mutant proteins (B), as do the direct lysates (C). Grg4 expressing lysates also show similar levels of this protein (D). Note: Although the co-expression of Grg4 along with the wild-type and mutant Fox constructs shows similar protein levels and binding in the IPs, it is worth noting that there is a marked reduction in expression of all Fox proteins in the presence of Grg4. This may be due to degradation, rather than competition for ribosomes that affects translation, since Grg4 levels are not affected.