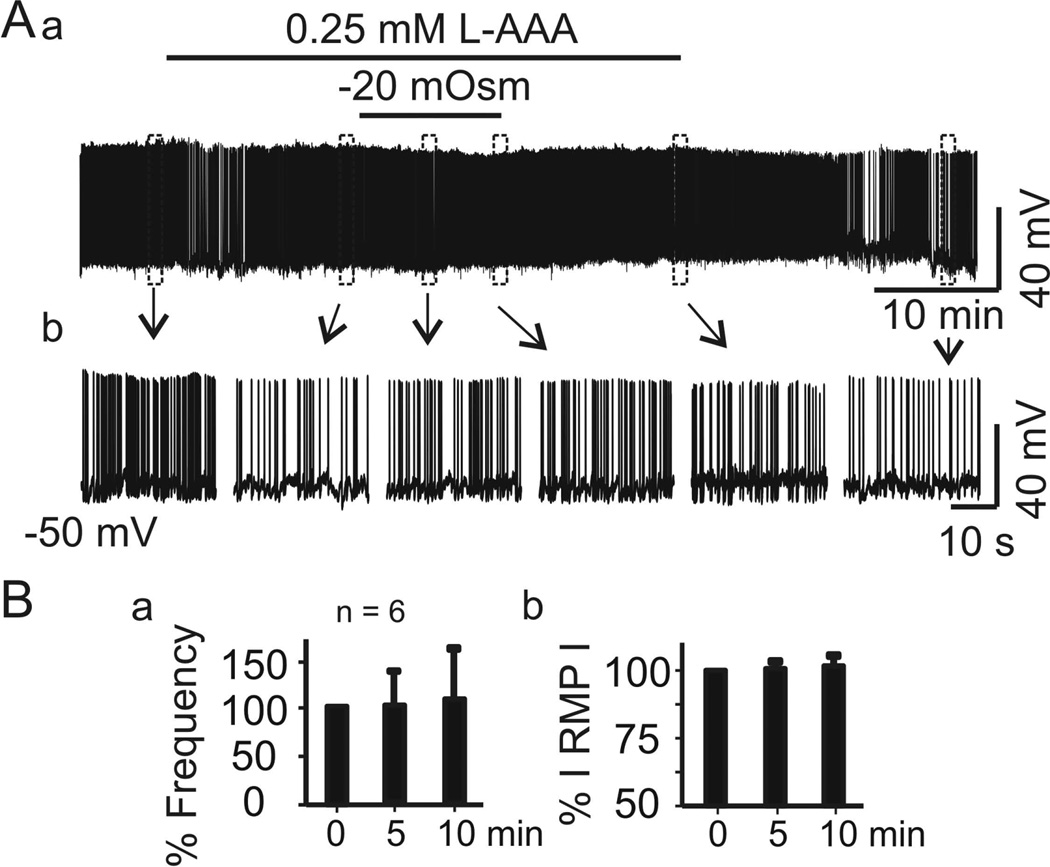
Figure 3.
Disruption of astrocyte functions blocks hypoosmotic suppression or later recovery of vasopressin neurone firing. A, Firing activity of a vasopressin neurone in naCSF containing the gliotoxin l-aminoadipic acid (L-AAA, 0.25 mM) before and after superfusion with haCSF containing L-AAA, in full recording (Aa) and expanded episodes (Ab). B, Mean ± SEM changes (%) in firing rate (Ba) and absolute value of the membrane potential (RMP, Bb) of 6 cells after 5 and 10 min superfusion, relative to 0 min. No significant differences were observed.