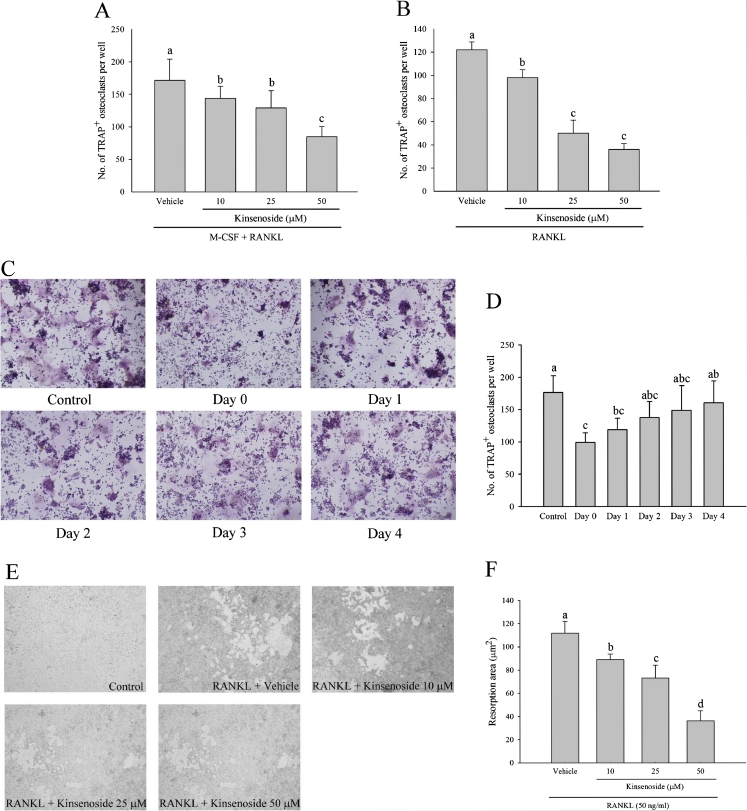
Fig. 3.
Kinsenoside inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption. a BMs were cultured with the indicated dose of kinsenoside in the presence of M-CSF and RANKL. After 9 days, cells were fixed and stained with TRAP. Multinucleated osteoclasts were counted. b RAW 246.7 cells were cultured with the indicated dose of kinsenoside in the presence of RANKL. After 5 days, cells were fixed and stained with TRAP. Multinucleated osteoclasts were counted. c Kinsenoside inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis at an early stage. The TRAP stains of osteoclasts were treated with kinsenoside (50 μm) at the same time or after indicated time periods. Cells were cultured for 5 days after RANKL treatment and stained for TRAP expression. Multinucleated osteoclasts were counted. The quantitative data are shown in d. e RAW 246.7 cells plated on BD BioCoat™ Osteologic™ and incubated with different concentrations of kinsenoside in the presence of RANKL (50 ng/ml) for 7 days. Cells were removed by washing with distilled water and resorbed areas were measured. The quantitative data are shown in f. All values are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). Values not sharing a common superscript differ significantly. c ×100