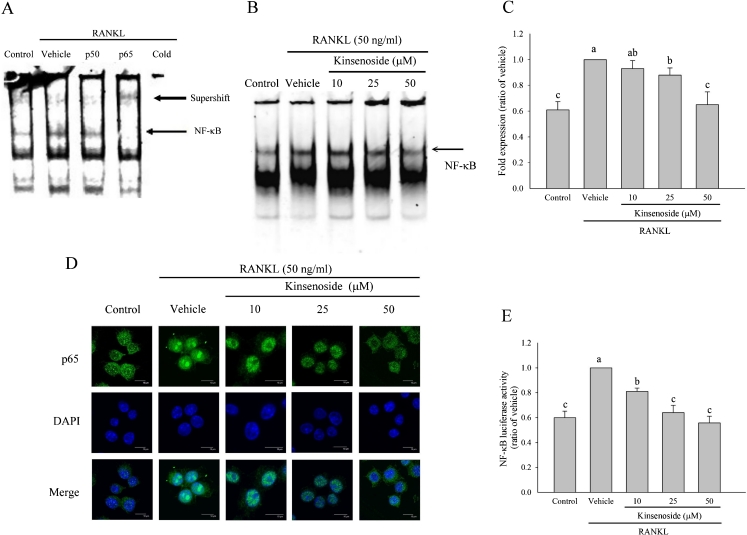
Fig. 4.
Kinsenoside inhibited RANKL-induced transcriptional activity of NK-κB in RAW 264.7 cells. a EMSA results showed a supershift of complex formed in the presence of anti-p50 and anti-p65 antibodies. The p65 subunits cause a specific binding of NF-κB to consensus DNA sequence. Cold the nuclear extract was preincubated with an excess of unlabeled oligonucleotide. b RAW 264.7 cells were incubated with or without the indicated concentrations of kinsenoside for 2 h and then treated with RANKL for 1 h and tested for nuclear NF-κB by EMSA. The quantitative data are shown in c. d RAW 264.7 cells were pretreated with kinsenoside and then stimulated with RANKL for 1 h. The localization of p65 was visualized by immunofluorescence analysis. e RAW 264.7 cells were transiently transfected with an NF-κB promoter plasmid for 16 h. After transfection, the cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of kinsenoside for 2 h and then treated with RANKL for an additional 24 h. Cells were lysed, and the luciferase activity was determined by using a luciferase reporter assay system. Values are expressed as means ± SD (n = 3). Values not sharing a common superscript differ significantly