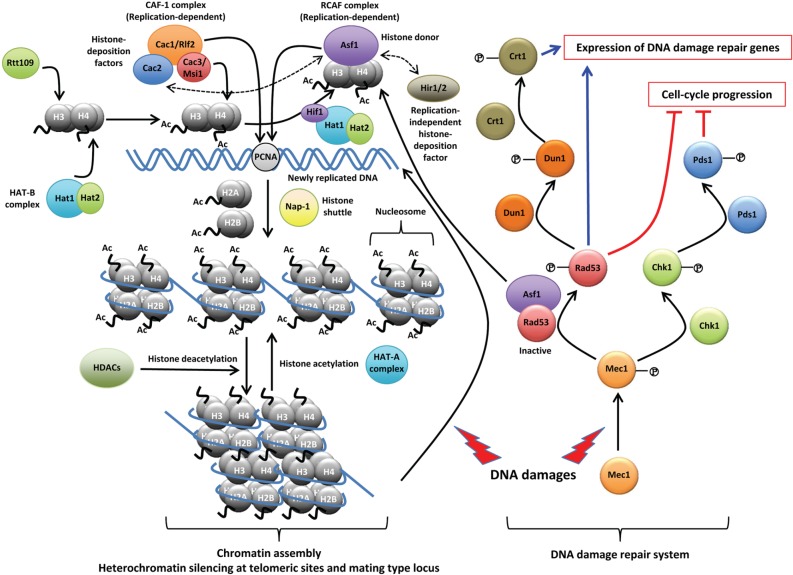
Fig. 1.
The proposed roles of Msi1-like (MSIL) proteins in chromatin assembly and DNA damage repair. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, two MSIL proteins, histone acetyltransferase 2 (Hat2) and Cac3/Msi1, are primarily involved in nucleosome assembly and chromatin assembly. As a component of the histone acetyltransferase B (HAT-B) complex, Hat2 assists Hat1, which binds to and acetylates newly synthesized histone H4. Then, the HAT-B complex transfers the histone H3/H4 tetramer into the nucleus. In the nucleus, the HAT-B complex forms a NuB4 complex, which delivers the H3/H4 tetramer to anti-silencing function 1 (Asf1) by interaction with the Hat1p-interacting factor 1 (Hif1) histone chaperone. The histone H3 in the delivered H3/H4 tetramer is acetylated by another nuclear histone, acetyltransferase Rtt109, associated with Asf1. As a histone chaperone, Cac3/Msi1 is the smallest subunit of the chromatin assembly factor 1 (CAF-1) complex, which additionally contains Cac1/Rlf2 (the largest subunit) and Cac2. CAF-1 is involved in chromatin assembly as a histone-deposition factor during DNA replication as well as DNA damage repair. The replication-coupled assembly factor (RCAF), composed of Asf1 and an acetylated tetramer of H3/H4, serves as a histone donor and also plays overlapping roles with CAF-1 in chromatin assembly during DNA replication. Histon regulatory (Hir) 1 and Hir2 are also histone-deposition factors, which act independently from DNA replication. Asf1 can interact with the Cac2 of CAF-1 and Hir1/2. CAF-1 assembles histone H3/H4 onto newly replicated DNA by targeting proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Two dimers of histones H2A and H2B are transferred by the nucleasome assembly protein 1 (Nap-1) which shuttles between the cytoplasm and the nucleus. Histone deacetylation by histone deacetylases (HDACs) facilitates aggregation of the nucleosome and results in chromatin assembly. This complex, compact structure of chromatin provides the basis for heterochromatin gene silencing at telomeric regions and mating type locus. When DNA damage occurs, such as double-strand DNA breaks, histones in the chromatin structure are dissociated and a series of DNA-repair signaling cascades, including Mec1, Rad53, Chk1, Pds1, Dun1, and Crt1, are activated to induce the expression of genes involved in DNA damage repair and to block the progression of cell-cycle. Notably, Asf1 physically interacts with Rad53 under normal conditions, and upon DNA damage, Asf1 and Rad53 phosphorylated by Mec1 are released, serving as a histone donor and activator of the DNA damage repair system, respectively. PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen. For more detailed information, please refer to the following review [30].