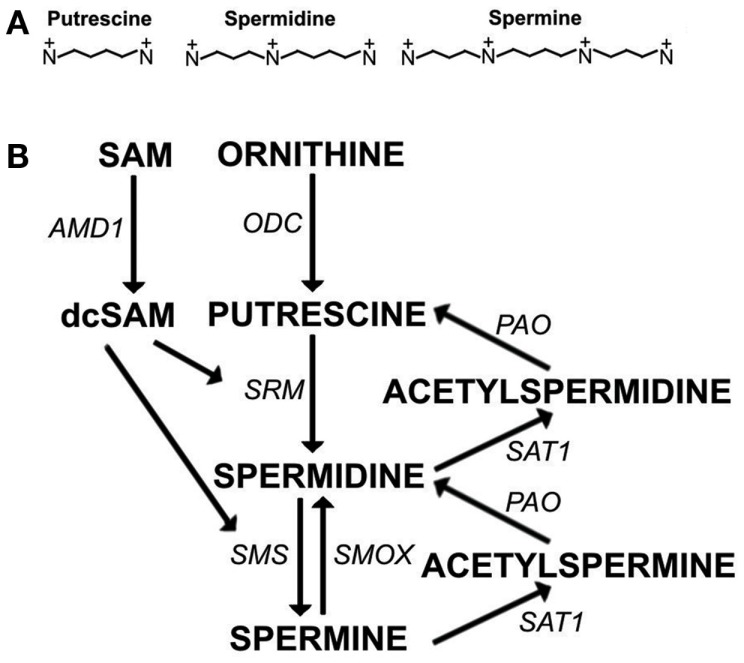
Figure 1.
The polyamine pathway. (A) Polyamines at physiological pH: Putrescine (+2, ∼8Å), Spermidine (+3, ∼12Å), Spermine (+4, ∼16Å). (B) Polyamine synthesis and recycling. S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase (AMD1) and ornithine decarboxylase (ODC) are rate limiting steps in polyamine synthesis. AMD1 decarboxylates S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) to decarboxylated SAM (dcSAM) so that dcSAM can provide aminopropyl groups added to putrescine to make spermidine by spermidine synthase (SRM) and added to spermidine to make spermine by spermine synthase (SMS). Spermine can be recycled to spermidine directly by spermine oxidase (SMOX). Spermine and spermidine can be recycled to spermidine and putrescine, respectively, by spermidine/spermine-N1-acetyltransferase (SAT1) followed by oxidation by polyamine oxidase (PAO).