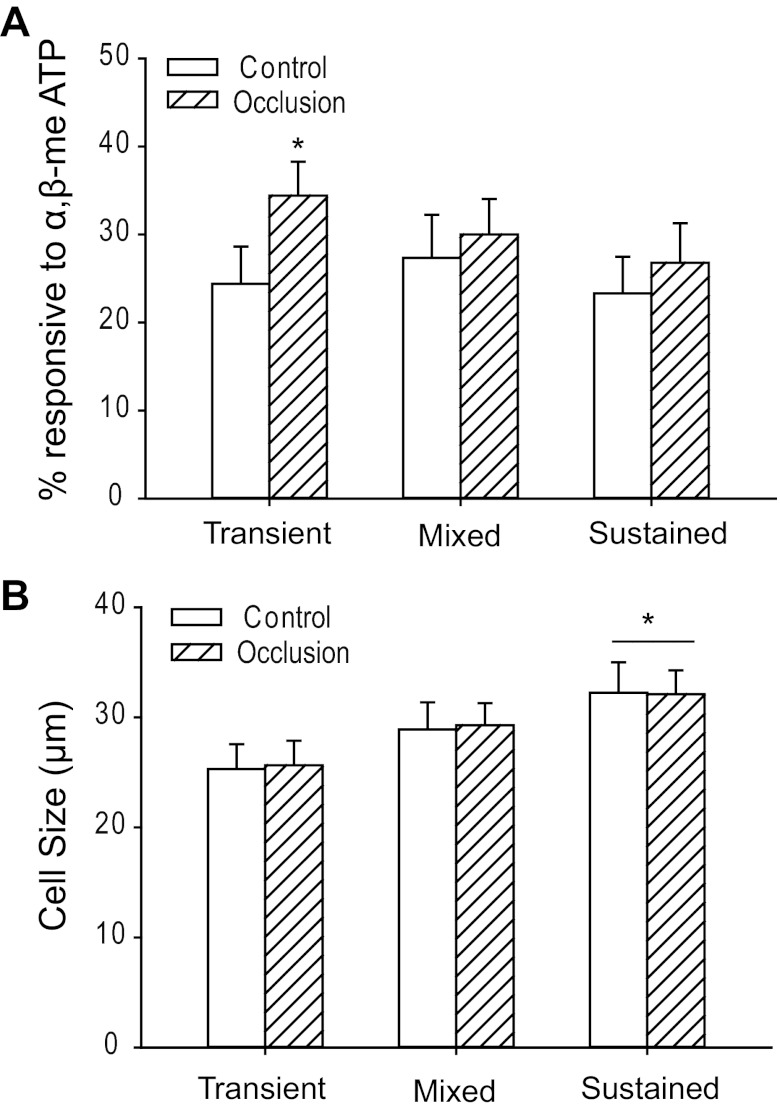
Fig. 2.
Percentage and size distribution of DRG neurons responding to α,β-meATP. A: percentage of DRG neurons innervating muscle with 3 different types of currents responsive to α,β-meATP in control limbs and limbs with occlusion. A larger percentage of DRG neurons with transient currents was observed after 24 h of arterial occlusion than in control. *P < 0.05 vs. control. The percentages of cells with mixed currents (P = 0.99, control vs. occlusion) and sustained currents (P = 0.98, control vs. occlusion) were not significantly changed by 24-h femoral occlusion. B: diameters of DRG neurons innervating muscle responding to α,β-meATP in control limbs and limbs with occlusion. Averaged data show mean diameters of cells with fast-inactivating currents were significantly smaller than those of cells with sustained currents in both control and occlusion groups. *P < 0.05, transient vs. sustained currents for both control and occlusion groups. There were no significant differences of cell size of DRG neurons between the groups with transient currents and mixed currents (P = 0.48 in control; P = 0.23 in occlusion) and between the groups with mixed currents and sustained currents (P = 0.58 in control; P = 0.57 in occlusion). No differences were observed for the average size of DRG neurons that responded to α,β-meATP with fast, mixed, or sustained currents between both control and occlusion groups.