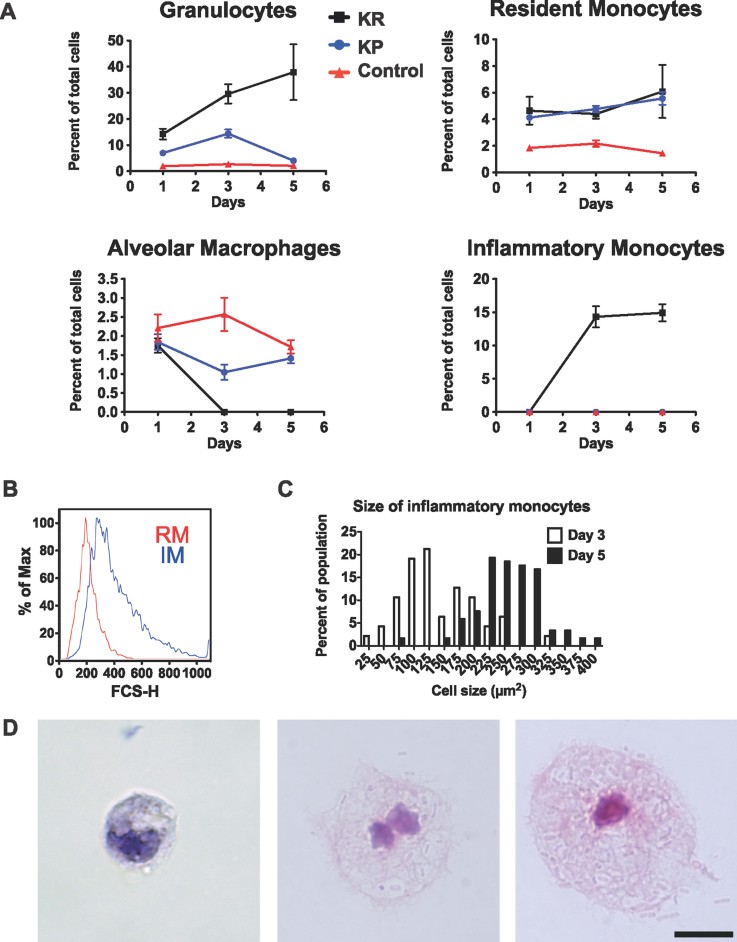
Figure 2.
Kinetics of cells recruitment after infection with K. rhinoscleromatis and Kp52.145.
A. Lung cells of BALB/c mice infected with 2.107 K. rhinoscleromatis, 2.104 Kp52.145 or saline-injected controls were isolated 1, 3 and 5 days post inoculation and stained for granulocytes (Gr1+ F4/80− CD11b+ CD11c−), resident monocytes (Gr1− F4/80+ CD11b+ CD11c−), alveolar macrophages (Gr1- F4/80+ CD11b− CD11c+) or inflammatory monocytes (Gr1+ F4/80+ CD11b+ CD11c−). Results show the percentage of each cell population among the total lung cells. Data are mean ± SEM and represent between 6 and 12 mice for each point from at least three independent experiments.
B. Forward scatter histogram of resident monocytes (RM, red) and inflammatory monocytes (IM, blue).
C. Quantification of sorted inflammatory monocytes size. Cell size was measured 3 (white bars, n = 49) and 5 (black bars, n = 119) days post-infection.
D. Three and five days post-infection by K. rhinoscleromatis, cells were isolated and the inflammatory monocyte population was sorted by FACS, centrifuged onto slides and stained with HE. Classical monocytes (left) and small Mikullicz cells (middle) were observed 3 days post-infection. Large Mikulicz cells (right) were present 5 days post infection. Scale bar: 10 µm.