Fig. 8.
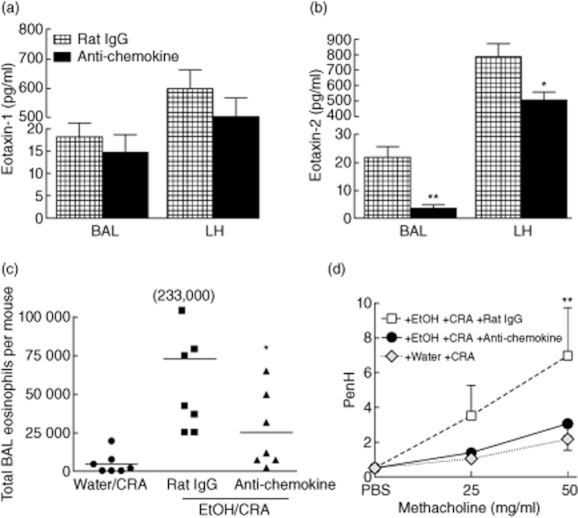
Chemokine-neutralizing antibodies prevent ethanol-induced eosinophil recruitment and airways hyperreactivity (AHR). Ethanol-gavaged and cockroach allergen (CRA)-challenged mice were treated with a cocktail of anti-chemokine antibodies or control rat immunoglobulin (Ig)G 2 h prior to CRA challenge. Mice were killed at 1·5 h post-CRA challenge at the height of eosinophil recruitment or 14 h for AHR measurement. (a) Eotaxin-1 was reduced slightly in both lung compartments, although not significantly. (b) Eotaxin-2 was significantly lower in the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) and lung homogenate (LH) of mice receiving chemokine-neutralizing antibodies. (c) BAL eosinophils. Administration of chemokine neutralizing antibodies decreased BAL eosinophil infiltrate. Each symbol represents an individual mouse and the horizontal bar is the mean. The 233 000 is a single mouse whose value did not fit onto the scale. (d) AHR. Development of AHR was prevented in mice receiving chemokine-neutralizing antibodies. Data are mean ± standard deviation of the mean for three to eight mice from two separate experiments. *P < 0·05, **P < 0·01 anti-chemokine compared to control rat IgG.
