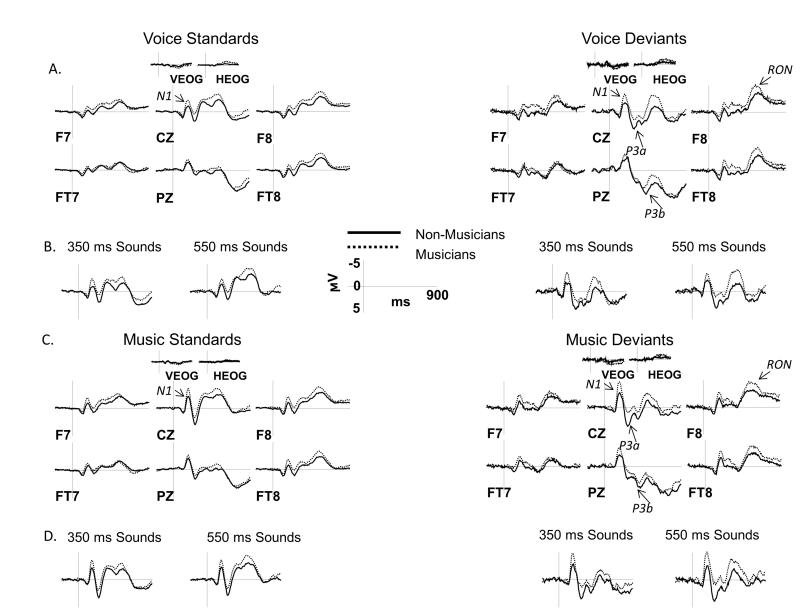
Figure 5.
ERP results in the NAT condition: musicians vs. non-musicians
ERPs elicited by musical and vocal sounds in the NAT condition are shown over a representative set of electrodes. A, C: ERPs from musicians are overlaid with those from non-musicians separately for standards (left side) and deviants (right side) and for vocal (panel A) and musical (panel C) sounds. ERPs were averaged across short and long sound durations for all comparisons. B, D: Separate ERP grand averages for short (350 ms) and long (550 ms) sounds are shown at the CZ site for vocal (panel B) and musical (panel D) sounds. Analyzed ERP components are marked on multiple electrode sites. Negative potentials are plotted upward. Time 0 ms indicates the onset of the stimulus.