Fig. 1.
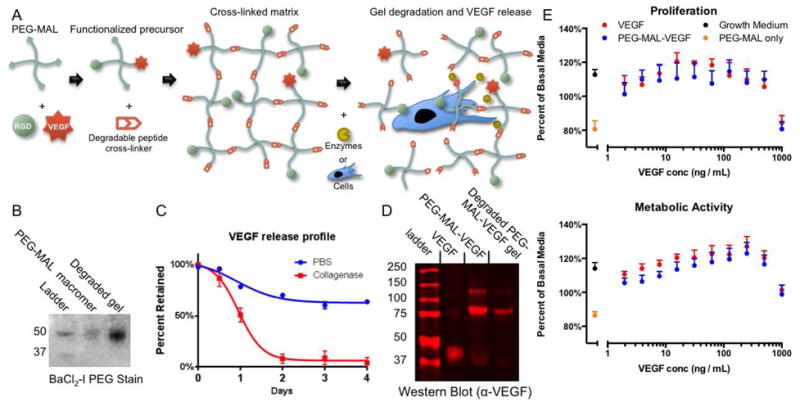
PEG-MAL hydrogels for on-demand release of VEGF. (A) 4-arm PEG-MAL macromer is functionalized by maleimide-thiol Michael-type addition reactions with RGD peptide and VEGF growth factor. The matrix is cross-linked by a cysteine-flanked degradable peptide cross-linker GCRDVPMSMRGGDRCG. Proteases or protease-expressing cells degrade the hydrogel by cleaving cross-linker peptides and release VEGF. (B) BaCl2-I stain for PEG showing MW of PEG-MAL precursor and gel degradation product. (C) VEGF release profile from degrading gels or gels treated in PBS as measured by ELISA (± S.E.M. n=6). (D) Western blot of PEG-MAL-VEGF functionalized precursor or gel degradation product compared to native VEGF showing molecular weight change of VEGF once PEGylated. (E) Endothelial cell proliferation assay for VEGF vs. PEG-MAL-VEGF bioactivity measured by metabolic activity (MTS) and proliferation (EdU incorporation) (± S.E.M. n=6).
