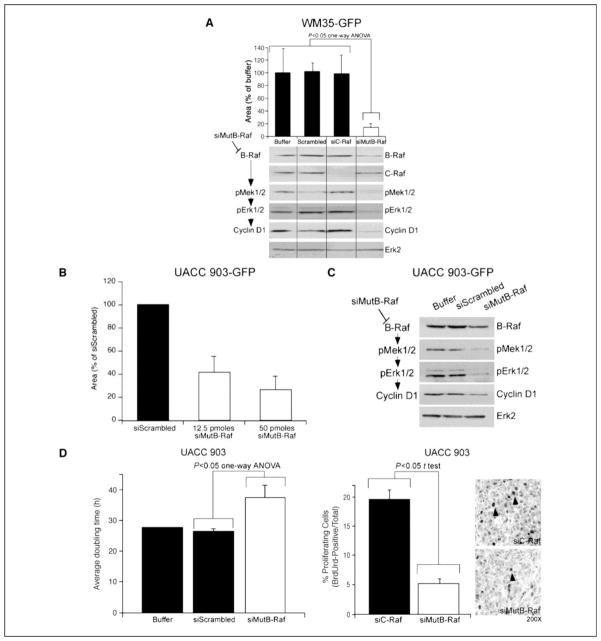
Figure 5. siMutB-Raf inhibits melanocytic lesion growth in reconstructed skin.
A. Targeting melanocytic lesions using siRNA against V600EB-Raf decreases melanocytic lesion development in laboratory-generated skin. Effectiveness of siRNA targeting V600EB-Raf for decreasing cutaneous tumor development was established by nucleofecting GFP-tagged WM35 cells with buffer, scrambled siRNA or siRNA targeting C-Raf, or V600EB-Raf (100 pmoles). Cells were then seeded into laboratory-generated skin at time of creation and 10 d later, average area occupied by green melanocytic lesions quantified. A statistically significant reduction in green fluorescent lesions was observed following siMutB-Raf treatment (p<0.05; One-Way ANOVA) (upper panel). Results are mean±SE. Protein lysates harvested from cells were analyzed by Western blot for B-Raf, C-Raf, p-Mek1/2, pErk1/2, and Cyclin D1 protein expression. Erk2 served as a control for protein loading (lower panel). B. siRNA-mediated inhibition of V600EB-Raf protein expression in GFP-tagged UACC 903 cells decreases lesion formation in skin reconstrtucts. UACC 903-GFP cells were nucleofected with siScrambled or siB-Raf (12.5 or 50 pmoles) and cells seeded into laboratory generated skin at time of creation. Reconstructed skin was analyzed using fluorescence microscopy 10 d later and area occupied by developing GFP lesions quantified. Results are mean±SE. C. Inhibition of V600EB-Raf decreased MAP kinase signaling in UACC 903-GFP cells. UACC 903-GFP cells were nucleofected with buffer, siScrambled or siB-Raf (50 pmoles) and harvested at 48 h for Western blot analysis. Westerns were probed with B-Raf, p-Mek1/2, p-Erk1/2, and cyclin D1 to show decreased MAP kinase pathway signaling. Erk2 served as a loading control. D. Mechanistically, siRNA-mediated targeting of V600EB-Raf protein decreased the proliferative capacity of cells. Cultured UACC 903 melanoma cells treated with siMutB-Raf had an increased doubling time indicating cells were proliferating at a slower rate (left panel). Quantifying proliferating cells showed a 2–3 fold decrease following siMutB-Raf treatment of tumor cells in size and time matched tumor controls treated with siRNA to C-Raf (middle and right panels). Results are mean±SE.