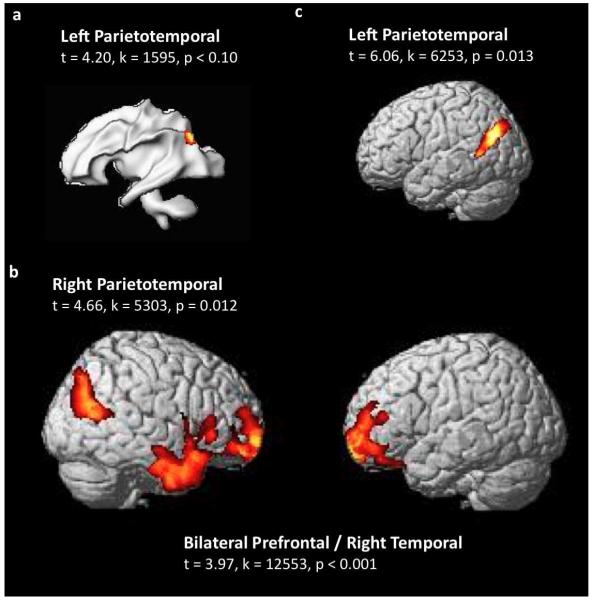
Figure 3. Association between regional brain volume and maternal Family Risk Index (mFamRI; FamRI is equivalent to Adult Reading History Questionnaire [ARHQ] scores).
a. Brain region where there was a trend for significant negative association between white matter volume (WMV) and mFamRI (0.05<p<0.1 corrected). This region was not significant when the Behavioral Risk Index (BxRI; defined as a composite of letter identification [LID], rapid naming [RN] and phonological awareness [PA] scores) was entered as a nuisance variable (p>0.1 corrected). Main region and statistical values (t-values, cluster size in voxels [k] and p values) are listed.
b. Brain regions where there were significantly reduced grey matter volume (GMV) in children with mFamRI compared to those without based on ARHQ scores (p<0.05 corrected). Note similarities with Figures 2a and 2b in bilateral prefrontal cortices and right parieto-temporal regions. Note also the lack of left parieto-temporal region (t=3.69, k=2425, p=0.13 corrected), and addition of the right temporal regions.
c. Brain regions where there were significantly reduced GMV in children with a maternal family history of reading disability compared to those with paternal family history based on ARHQ scores (p<0.05 corrected). Note spatial overlap with the left parieto-temporal region in Figure 2a.