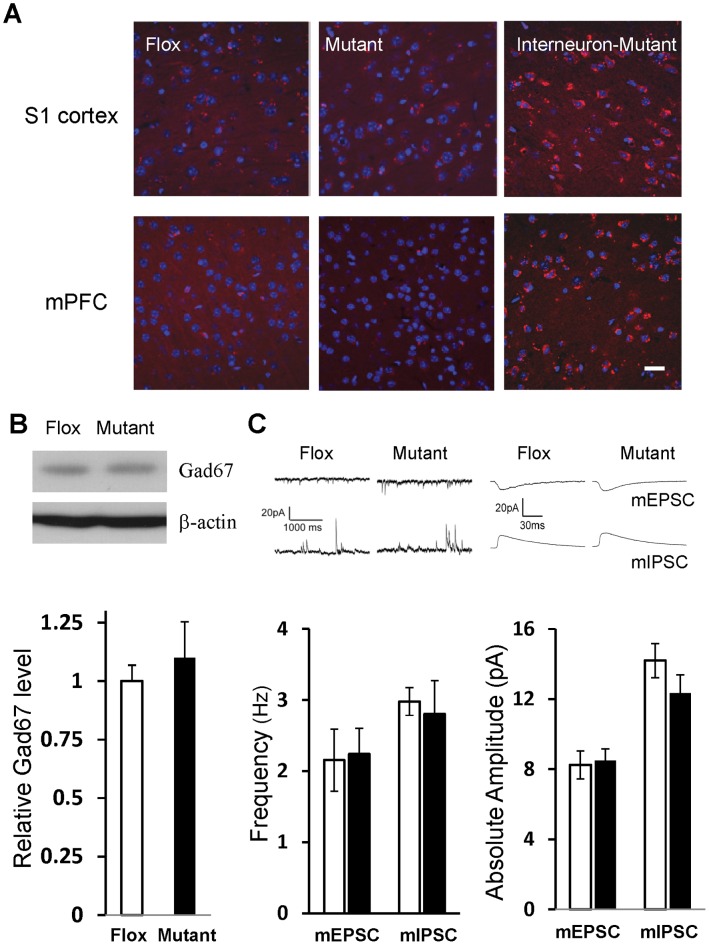
Figure 8. Reactive oxygen species’ level and GABAergic inhibition.
A. Fourteen-week-old mice received injection of dihydroethidium to assess reactive oxygen species (ROS) levels. ROS levels, visualized by red fluorescence, were negligible in cortical sections of somatosensory cortex (upper) and medial prefrontal cortex (lower) in both Flox and CtxGluN1KO mutant mice. Right panels are sections from adult corticolimbic interneuron-GluN1 knockout mice (Ppp1r2-Cre/GluN1 KO mice) as a positive control. Scale Bar: 100 µm. B. Gad67 protein levels in cortical homogenates (6 animals for each group) were examined by Western blot. Gad67-IR intensity was normalized by the β-actin–IR on the same gel. No genotypic difference was detected in Gad67 protein levels. Student’s t-test, p = 0.56. C. Properties of miniature EPSC (mEPSC) and miniature-IPSC (mIPSC) events in mPFC layer II/III pyramidal neurons. The data of 2–3 cells were collected from single animal and averaged per animal (animal number, n = 6 for Flox (white bar), n = 7 for mutant (black bar)). No genotypic differences were observed in frequencies or amplitudes of both measures. Student’s t-test, p = 0.88 for mEPSC frequency, p = 0.97 for mIPSC frequency, p = 0.81 for mEPSC amplitude, p = 0.37 for mIPSC amplitude.